With the growth of virtualization, cloud-based services and applications like VoIP, video streaming and IP surveillance, SMB networks need to extend beyond simple reliability to higher speed and performance. The NETGEAR ProSAFE XS712T and ProSAFE XS728T switches present the right solution for this requirement, delivering unprecedented non-blocking 10G bandwidth at an affordable cost. Have you ever used NETGEAR 10Gb switch in your network? This article may provide the knowledge of NETGEAR 10G switch deployment and its interface requirement.
NETGEAR 10G Switch Overview
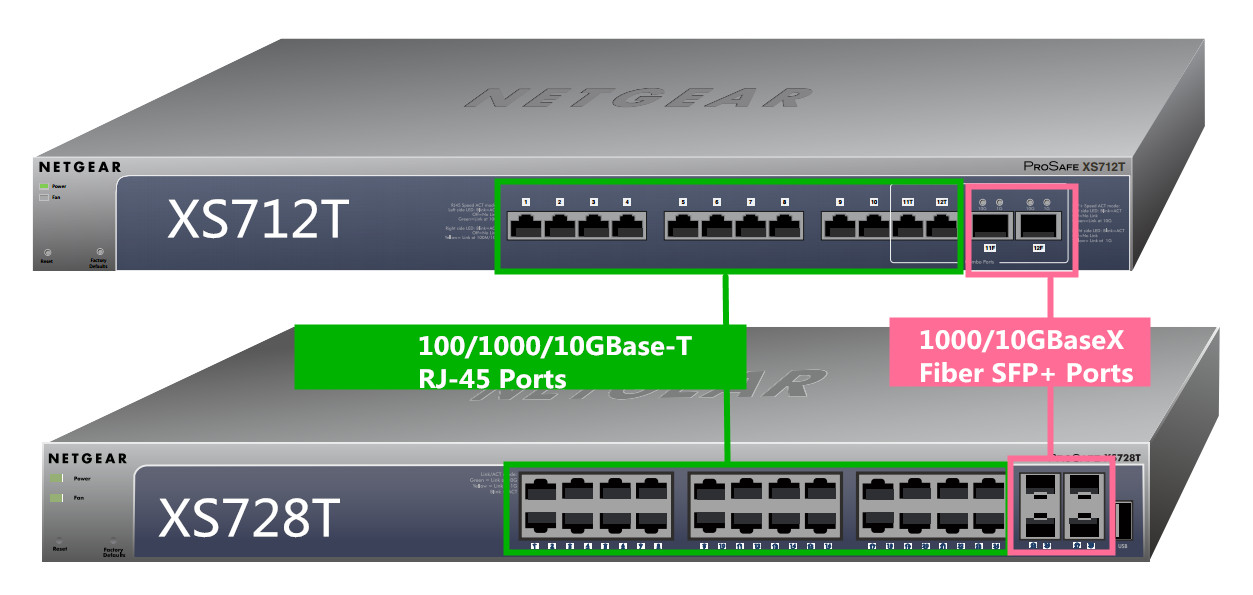
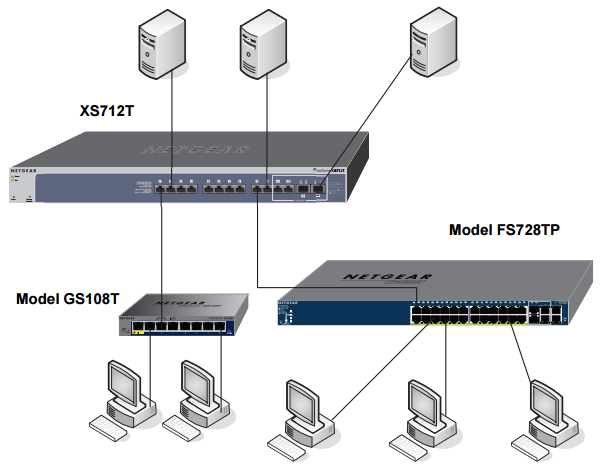
As shown in the figure below, the NETGEAR ProSAFE XS712T and ProSAFE XS728T are powerful smart managed switches that come with either 12 or 24 10G copper ports and either 2 combo SFP+ (XS712T) or 4 additional dedicated SFP+ ports (XS728T) for 10G fiber links. Using these 10G slots, you can create high-speed connections to a server or network backbone. For example, you can connect switches to each other with high-speed links or link them to high-speed servers. Please note that the XS712T can provide 100M/1000M/10G copper connectivity, but the XS728T can only provide 1000M/10G copper connectivity. Fast Ethernet is not available for XS728T switch.
How to Connect NETGEAR 10G Switch to Your Network?
The NETGEAR ProSAFE XS728T and XS712T switch is designed to provide flexibility in configuring your network connections. It can be used as your only network traffic-distribution device or with 100 Mbps (XS712T only ) , 1000 Mbps, and 10 Gbps hubs and switches.
- Connecting devices to the switch via RJ-45 copper port
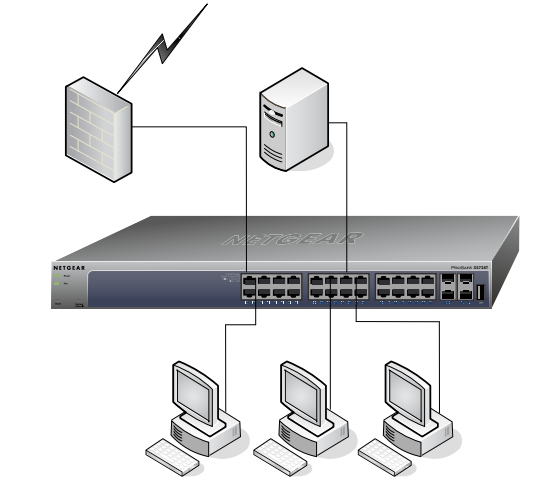
The RJ-45 copper ports of the NETGEAR ProSAFE 10G series switch comply with IEEE 10GBase-T standards. It is backward compatible, auto-negotiating between higher and lower speeds. You can use Category 5e (CAT 5e) or better Ethernet cable (CAT 6, CAT 6a, or CAT 7) to make 10G connections. AMONG, CAT5/CAT5E are supported for Gigabit speeds up to 100 meters. CAT6 twisted pair copper cabling supports 10-Gigabit speeds up to 45 meters. CAT6A or newer CAT7 cabling will allow for up to 100 meter 10GBase-T connections. Desktop switching of NETGEAR ProSAFE XS728T is shown in the figure below.
- Connecting devices to the switch via SFP+ fiber port
To enable you to use fiber connections on your network (shown in the figure below) , two combo SFP+ ports of XS712T switch and four dedicated SFP+ ports of XS728T switch accommodate standard 1000M and 10G SFP+ transceiver modules. Please note that not all SFP or SFP+ transceiver modules are aavailable for NETGEAR ProSAFE 10G series switch. Following table may give you some guidance for transceiver modules option.
SFP /SFP+ transceiver modules and SFP+ cables supported for ProSAFE XS712T and XS728T switch
| MFG PART# | Description |
| AGM731F | NETGEAR 1000BASE-SX 850nm SFP, up to 550m |
| AGM732F | NETGEAR 1000BASE-LX 1310nm SFP, up to 10km |
| AXM761 | NETGEAR 10GBASE-SR 850nm SFP+, up to 300m |
| AXM762 | NETGEAR 10GBASE-LR 1310nm SFP+, up to 10km |
| AXM763 | NETGEAR 10GBASE-LRM 1310nm SFP+, up to 220m (XS712T only) |
| AXM764 | NETGEAR10GBASE-LR Lite 1310nm SFP+, up to 2km |
| AXC761 | 1m NETGEAR SFP+ to SFP+ Passive Copper Cable |
| AXC763 | 3m NETGEAR SFP+ to SFP+ Passive Copper Cable |
 Small Package Makes Sense
Small Package Makes Sense 2.1bn by 2019.
2.1bn by 2019.