When install a fiber optic network, people may make some common mistakes, which were usually overlooked. In this article, I will list the most common ones. Hope to give you some guidance for your optical network installation.
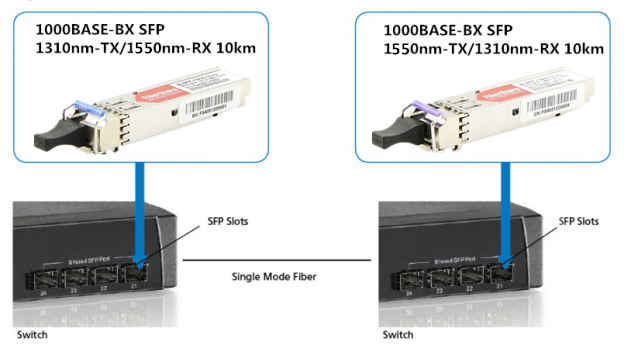
You will never buy two left shoes, but people often make a similar mistake when they’re working with Single Strand Fiber (SSF). Single strand fiber technology allows for the use of two independent wavelengths, such as 1310 and 1550 nm, on the same piece of cable. The most common single strand fiber device is Bi-Directional (BiDi) transceiver. Two BiDi transceiver must be matched correctly. One unit must be a 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX transceiver (transmitting at 1310 nm, receiving at 1550 nm) and the other must be a 1550nm-TX/1310nm-RX transceiver (transmitting at 1550 nm, receiving at 1310 nm). The 1550nm-TX/1310nm-RX transceiver is more expensive than the 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX transceiver, due to the cost of their more powerful lasers. So network engineers may hope to save money by installing a pair of 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX transceivers. But, like mismatched shoes, it doesn’t work.
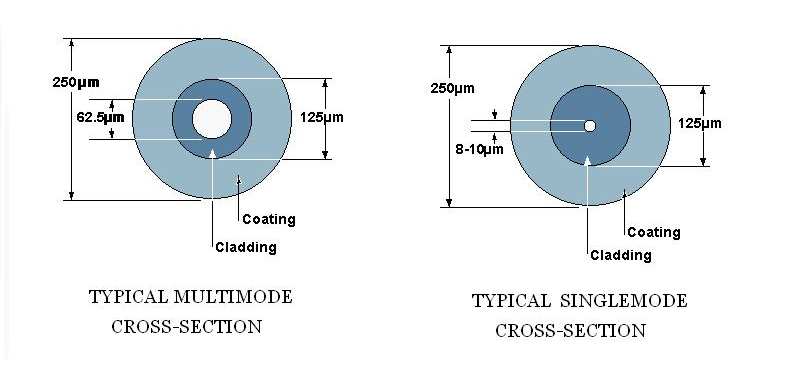
Some people may want to make use of legacy cabling or equipment from an older fiber installation to save cost. But keep in mind that single-mode and multimode fiber are usually incompatible. Multimode fiber uses cable with a relatively large core size, typically 62.5 microns (om2, om3 and om4), and 50 microns (om1) still used in some installations. The larger core size simplifies connections and allows for the use of less powerful, less expensive light sources. But the light therefore tends to bounce around inside the core, which increases the modal dispersion. That limits multimode’s useful range to about 2 km. Single-mode fiber combines powerful lasers and cabling with a narrow core size of 9/125 microns to keep the light focused. It has a range of up to 120 km, but it is also more expensive. If you tried to use single-mode fiber over a multimode fiber run. The core size of the fiber cable would be far too large. You’d get dropped packets and CRC errors.
Fiber optic transceivers use a variety of connectors, so make clear their differences before you begin ordering products for a fiber installation is necessary. SC (stick and click) is a square connector. ST (stick and twist) is a round, bayonet-type. LC, or the “Lucent Connector”, was developed by Lucent Technologies to address complaints that ST and SC were too bulky and too easy to dislodge. LC connectors look like a compact version of the SC connector. SFP (small form‐factor pluggable) transceivers usually use LC connector. Less common connectors include MT-RJ and E2000.

Although single-mode fiber suffers from less signal loss per km than multimode, all fiber performance is affected by connectors and splices. The signal loss at a single connector or splice may seem insignificant. But as connectors and splices become more numerous signal loss will steadily increase. Typical loss factors would include 0.75 dB per connector, 1 dB per splice, 0.4 dB attenuation per km for single-mode fiber and 3.5 dB attenuation per km for multimode fiber. Add a 3 dB margin for safety. The more splices and connectors you have in a segment, the greater the loss on the line.
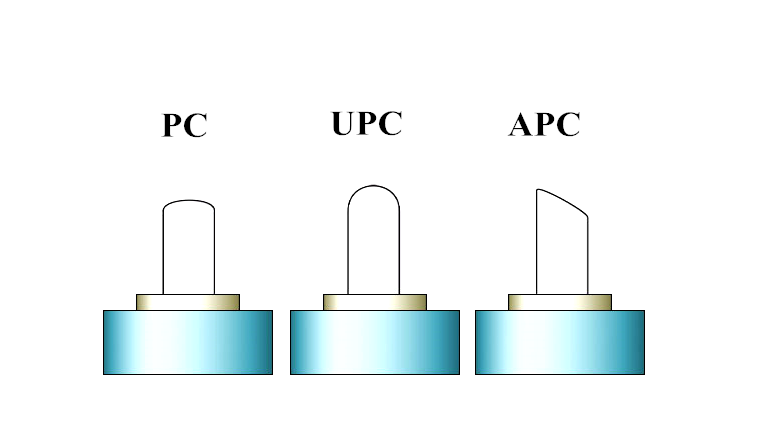
Fiber connections may use Angle Polished Connectors (APC) or Ultra Polished Connectors (UPC), and they are not interchangeable. There are physical differences in the ferules at the end of the terminated fiber within the cable (shown in the figure below). An APC ferrule end-face is polished at an 8° angle, while the UPC is polished at a 0° angle. If the angles are different, some of the light will fail to propagate, becoming connector or splice loss. UPC connectors are common in Ethernet network equipment like media converters, serial devices and fiber‐based switches. APC connectors are typical for FTTX and PON connections. ISPs are increasingly using APC.
Small Form Pluggable (SFP) transceivers are more expensive than fixed transceivers. But they are hot swappable and their small form factor gives them additional flexibility. They’ll work with cages designed for any fiber type and their prices are steadily dropping. So they have become very popular. Standard SFPs typically support speeds of 100 Mbps or 1 Gbps. XFP and SFP+ support 10 Gbps connections. SFP+ is smaller than XFP and allows for greater port density. Though the size of SFP and SFP+ is the same, you can’t connect SFP+ to a device (SFP) that only supports 1 Gbps.
Related Article: Optical Module Maintenance Methods and Installation Tips