There are many fiber patch cord types, such as OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 multimode fiber and OS2 single mode fiber types. Both ends of the cable are terminated with a high performance hybrid or single type connector comprising of a SC, ST, FC, LC, MTRJ, E2000 connector in simplex and duplex. These are typically not ruggedized, depending on the application, making them suitable for internal use. How to choose right fiber patch cord types for your network? Just follow these 6 steps.
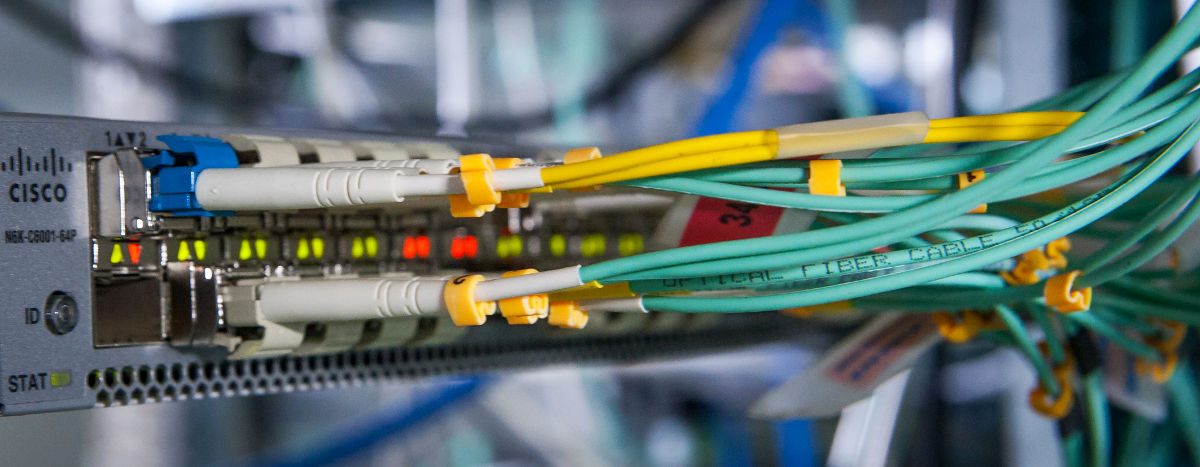
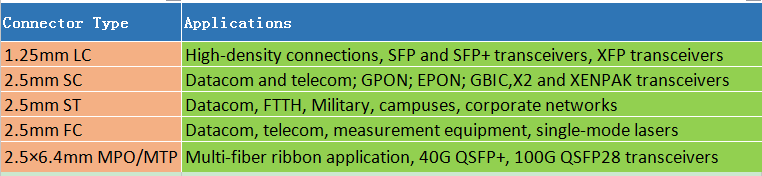
Step 1: Choose the Right Connector Type (LC/SC/ST/FC/MPO/MTP)
 On both ends of the fiber optic patch cord are terminated with a fiber optic connector (LC/SC/ST/FC/MPO/MTP). Different connector is used to plug into different device. If ports in the both ends devices are the same, we can use such as LC-LC/SC-SC/MPO-MPO patch cables. If you want to connect different ports type devices, LC-SC/LC-ST/LC-FC patch cables may suit you.
On both ends of the fiber optic patch cord are terminated with a fiber optic connector (LC/SC/ST/FC/MPO/MTP). Different connector is used to plug into different device. If ports in the both ends devices are the same, we can use such as LC-LC/SC-SC/MPO-MPO patch cables. If you want to connect different ports type devices, LC-SC/LC-ST/LC-FC patch cables may suit you.
Step 2: Choose Single-mode or Multimode Cable Type?
Single-mode fiber patch cord uses 9/125um glass fiber, Multimode fiber patch cord uses 50/125um or 62.5/125um glass fiber. Single-mode fiber optic patch cord is used in long distance data transmission. multimode fiber optic patch cord is use in short distance transmission. Typical single-mode fiber optic patch cord used yellow fiber cable and multi mode fiber optic patch cord used orange or aqua fiber cable.
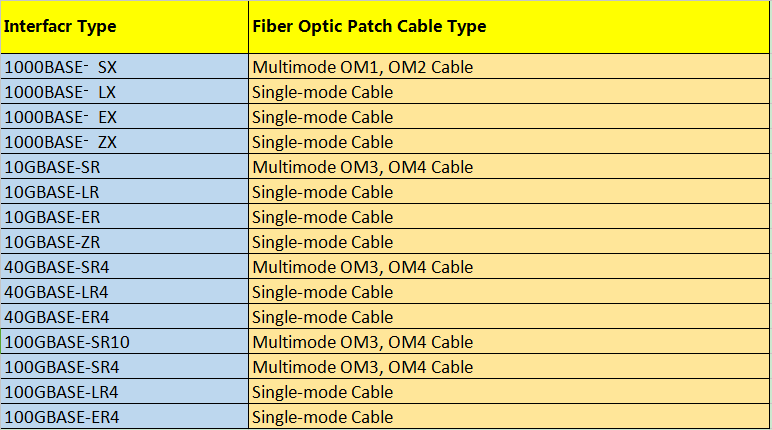
Step 3: Fiber Patch Cord Types – Choose Simplex or Duplex?
Simplex means this fiber patch cable is with one cord, at each end is only one fiber connector, which is used for Bidirectional (BIDI) fiber optic transceivers. Duplex can be regarded as two fiber patch cable put side by side, which is used for common transceivers.

Step 4: Choose the Right Cable Length (1m/5m/10m/20m/30m/50m)
Fiber optic patch cables are made in different lengths, usually from 0.5m to 50m. You should choose an appropriate cable length according to the distance between the devices you want to connect.
Step 5: Choose the Right Connector Polish Type (UPC/APC)
Since the loss of the APC connector is lower than UPC connectors, usually, the optical performance of APC connectors is better than UPC connectors. In the current market, the APC connectors are widely used in applications such as FTTx, passive optical network (PON) and wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) that are more sensitive to return loss. But APC connector is usually expensive than UPC connector, so you should weigh the pros and cons. With those applications that call for high precision optical fiber signaling, APC should be the first consideration, but less sensitive digital systems will perform equally well using UPC. Usually, connector color of APC patch cable is green, and of UPC patch cable is blue.

Step6: Choose the Right Cable Jacket Type (PVC/LSZH/OFNP/Armored)
Usually, there are three cable jacket types: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) and Optical Fiber Nonconductive Plenum (OFNP). You can see there features in figure below and choose the right one for your network.
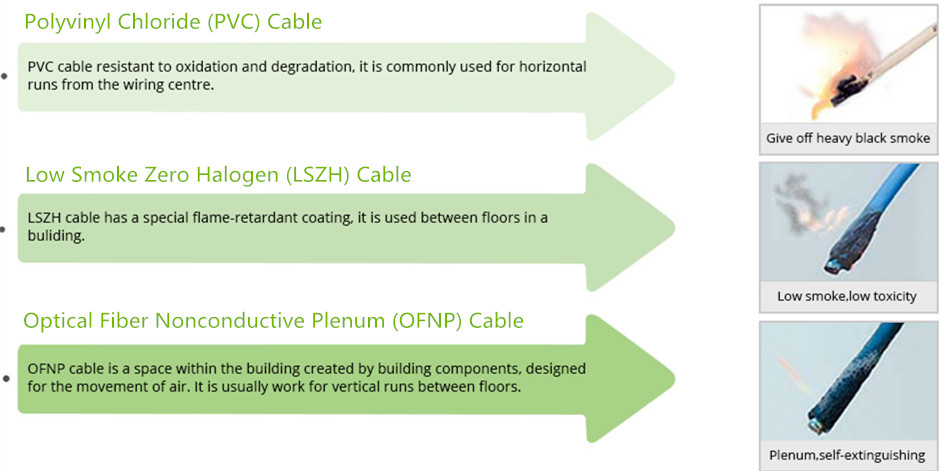
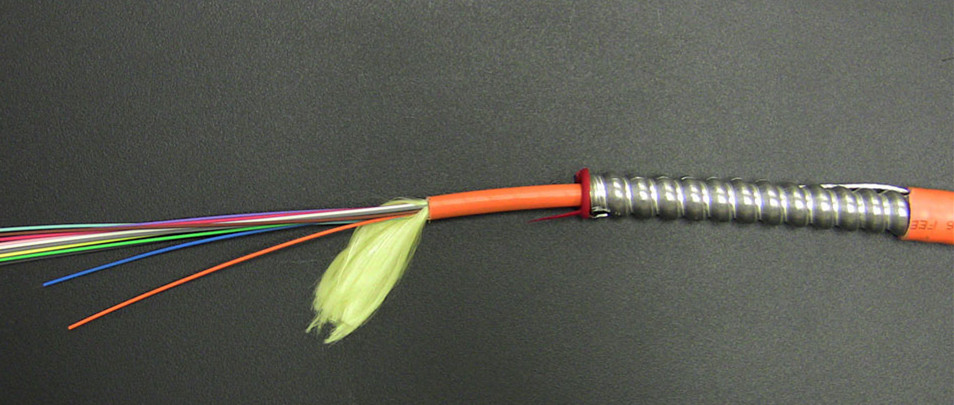
Besides the three cables mentioned above, there is another common cable—Armored Cable. The double tubing and steel sleeve construction make these patch cables completely light tight, even when bent. These cables can withstand high crushing pressures, making them suitable for running along floors and other areas where they may be stepped on. The tubing also provides excellent cutting resistance, abrasion resistance, and high tensile strength.

FS.COM provides all kinds of fiber optic patch cables to meet demands of various customers!
Related Article:
Common Types of Fiber Patch Cables
What Kind of Fiber Patch Cord Should I Choose?


