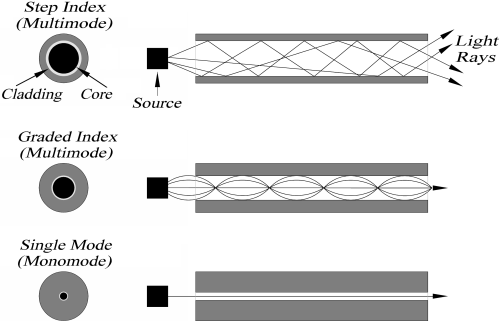
There are three common types of fiber optic cables , as listed below. The suitability of each type for a particular application depends on the fiber optic cable’s characteristics.
The single mode fiber optic cable, sometimes called a single-mode fiber cable, is shown in Figure 1.5(a). The single and multimode step-index fiber cables are the simpplest types of fiber optic cables. Single-mode fiber cables have extremely small core diameters, ranging from 5 to 9.5 um. The core is surrounded by a standard cladding diameter of 125 um. The jacket is applied on the cladding to provide mechanical protection, as shown in Figure 1.3. Jackets are made of one type of polymer in different colours for colour-coding purposes. Single-mode fibers have the potential to carry signals for long distances with low loss, and are mainly used in communication systems. The number of modes that propagate in a single-mode fiber depends on the wavelength of light carried. The number of modes will be given in Equation (1.9). A wavelength of 980nm results in multimode operation. As the wavelength is increased, the fiber carries fewer and fewer modes until only one mode remains. Single-mode operation begins when the wavelength approaches the core diameter. At 1310 nm, for example, the fiber cable permits only one mode. It then operates as a single-mode fiber cable.
The multimode types of fiber optic cables, sometimes called a multimode fiber cable. Multimode fiber cables have bigger diameters that their single-mode counerparts, with core diameters ranging from 100 to 970 um. They are available as glass fibers (a glass core and glass cladding), plastic-clas silica (a glass core and plastic cladding), and plastic fibers (a plastic core and cladding). They are also the widest ranging, although not the most efficient in long distances, and they experience higher losses than the single-mode fiber cables. Multimode fiber cables have the potential to carry signals for moderate and long distance with low loss (when optical amplifiers are used to boost the signals to the required power). Plastic fiber optic cable is available in Fiberstore, it is an optical fiber made out of plastic rather than traditional glass. It offers additional durability for uses in data communications, as well as decoration, illumination and industrial application. FiberStore provides both simplex and duplex plastic optical fibers.
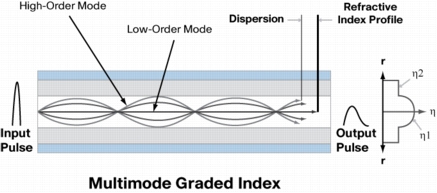
Since light rays bounded through a fiber cable reflect at different angles for different ray pathc, the path lengths of different modes will aslo be different. Thus, different rays take a shorter or longer time to travel the lenth of the fiber cable. The ray that goes straight down the centre of the core without reflecting arrives at the other end faster. Other rays take slightly longer and thus arrive later. Accoringly, light rays entering a fiber at the same time will exit at the other end at different times. In time, the light will spread out because of the different modes. This is called modal dispersion. Dispersion describes the spreading of light rays by various mechanisms. Modal dispersion is that type of dispersion that results from the varying modal patch lengths in the fiber cable.
Multimode graded-index fiber are sometimes called graded-index fiber cables (GRIN). Graded-index and multimode fiber cables have similar diameters. Common graded-index fibers have core diameters of 50,62.5, or 85 um, with a cladding diameter of 125 um. The core consist of numerous concentric layers of glass, somewhat like the annular rings of a tree or a piece of onion. Each successive layer expanding outward from the central axis of the core until the inner diameter of the cladding has a lower index of refrection. Light travels faster in an optical material that has a lower index of refraction. Thus, the further the light is from the centre axis, the greater its speed. These types of fiber optic cable are popular in applications that require a wide range of wavelenths, in particular telecommunication, scanning, imaging, and data processing stystems. In particular telecommunication, Multimode OM4 fiber optic cable is used in any data center looking for high speeds of 10G or even 40G or 100G. OM4 multimode fiber are ideal for using in many applications such as Local Area Networks (LAN) backbones, Storage Area Networks (SAN), Data Centers and Central Offices.
You may have got some basics of types of fiber optic cables. Fiberstore provides a wide range of types of fiber optic cable with detailed specifications displayed for your convenient selecting. Per foot price of each fiber cable is flexible depending on the quantities of your order, making your cost of large order unexpected lower. Customers can also have the flexibility to custom the cable plant to best fit their needs.
Related Article: The Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
Related Article: What Kind of Fiber Patch Cord Should I Choose?