There are different types of fiber optic cable. Some types are single-mode, and some types are multimode. Multimode fibers are described by their core and cladding diameters. Usually the diameter of the multimode fiber is either 50/125 µm or 62.5/125 µm. At present, there are four kinds of multi-mode fibers: OM1, OM2, OM3 and OM4. The letters “OM” stand for optical multimode. Each type of them has different characteristics.
Standard
Each “OM” has a minimum Modal Bandwidth (MBW) requirement. OM1, OM2, and OM3 fiber are determined by the ISO 11801 standard, which is based on the modal bandwidth of the multimode fiber. In August of 2009, TIA/EIA approved and released 492AAAD, which defines the performance criteria for OM4. While they developed the original “OM” designations, IEC has not yet released an approved equivalent standard that will eventually be documented as fiber type A1a.3 in IEC 60793-2-10.
Specifications
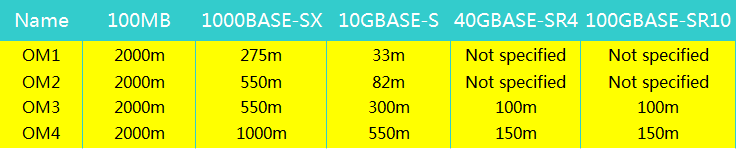
- OM1 cable typically comes with an orange jacket and has a core size of 62.5 micrometers (µm). It can support 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up 33 meters. It is most commonly used for 100 Megabit Ethernet applications.
- OM2 also has a suggested jacket color of orange. Its core size is 50µm instead of 62.5µm. It supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 82 meters but is more commonly used for 1 Gigabit Ethernet applications.
- OM3 fiber has a suggested jacket color of aqua. Like OM2, its core size is 50µm. It supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 300 meters. Besides OM3 is able to support 40 Gigabit and 100 Gigabit Ethernet up to 100 meters. 10 Gigabit Ethernet is its most common use.
- OM4 also has a suggested jacket color of aqua. It is a further improvement to OM3. It also uses a 50µm core but it supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up 550 meters and it supports 100 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 150 meters.
Differences
There are several differences between four kinds of multi-mode fiber, and we can see them clearly from the table below:
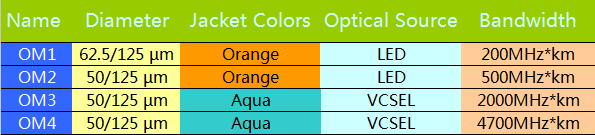
- Diameter: The core diameter of OM1 is 62.5 µm , however, core diameter of the OM2, OM3 and OM4 is 50 µm.
- Jacket Color: OM1 and OM2 MMF are generally defined by an orange jacket. OM3 and OM4 are usually defined with an aqua jacket.
- Optical Source: OM1 and OM2 commonly use LED light source. However, OM3 and OM4 usually use 850 nm VCSELs.
- Bandwidth: At 850 nm the minimal modal bandwidth of OM1 is 200MHz*km, of OM2 is 500MHz*km, of OM3 is 2000MHz*km, of OM4 is 4700MHz*km.
OM3 & OM4 are Superior to OM1&OM2
 Both OM1 and OM2 work with LED based equipment that can send hundreds of modes of light down the cable, while OM3 and OM4 are optimized for laser (eg. VCSEL) based equipment that uses fewer modes of light. LEDs can not be turned on/off fast enough to support higher bandwidth applications, while VCSELs are capable of modulation over 10 Gbit/s and are used in many high speed networks. For this reason, OM3 and OM4 are the only multi-mode fibers included in the 40G and 100G Ethernet standard. Now OM1 and OM2 are usually used for 1G which are not suitable for today’s higher-speed networks. OM3 and OM4 are used for 10G mostly at present. But in the future, since OM3 and OM4 can support the 40G and 100G, which may make them the tendency.
Both OM1 and OM2 work with LED based equipment that can send hundreds of modes of light down the cable, while OM3 and OM4 are optimized for laser (eg. VCSEL) based equipment that uses fewer modes of light. LEDs can not be turned on/off fast enough to support higher bandwidth applications, while VCSELs are capable of modulation over 10 Gbit/s and are used in many high speed networks. For this reason, OM3 and OM4 are the only multi-mode fibers included in the 40G and 100G Ethernet standard. Now OM1 and OM2 are usually used for 1G which are not suitable for today’s higher-speed networks. OM3 and OM4 are used for 10G mostly at present. But in the future, since OM3 and OM4 can support the 40G and 100G, which may make them the tendency.
Related article: Singl-mode vs. Multimode Fiber Cable