Introduction
With the spread of computer applications, along with the rapid development of network technology, the campus network has become an essential school information infrastructure. The implementation of the campus network, for schools to adapt to new developments and make fuller use of existing teaching resources for teching, management has provided a guarantee. Construction of intelligent building network as the physical basis. Using a variety of transmission media of the communication management device and the terminal connected. Its performance can affect the normal operation of the network and the length of life. Therefore, the design of a scientific and rational, optimized campus cabling system is to further play a variety of network equipment functions, the information and communication technologies to achieve the school a good development, improve the level of application management key.
The Campus Cabling System Overview
According to GB/T 50314 “Intelligent Building Design Standards” about the demarcation of ten categories of building regulations, school buildings, including ordinary full-time colleges and universities, high schools and senior vocational schools, junior and primary schools, nurseries and kindergartens school buildings, etc. Different levels of the school, its size, environment, personnel are different, so the campus cabling system requirements will be different.
The Campus Cabling System Features
In China, a full time ordinary institutions of higher learning, the campus area (not including campuses district), in general, nearly acres, some even a few acres. Distribution of number of buildings on campus and many species has a teaching building, comprehensive building, laboratory buildings, art building (including the campus theater, dance halls on campus, campus cultural centers), libraries, teachers’ apartments, student apartments, gymnasium, conference centers, schools’ hospitals, canteens and so on. Their application also includes teaching, testing, physical, network, accommodation, living, health care and other aspects. For colleges and universities this area, building scattered places different functions in the design of cabling, to be able to meet all of these different buildings, different application requirements, we need the entire cabling system to conduct a comprehensive in depth design considerations.
 Figure 1: Campus network design
Figure 1: Campus network design
On campus cabling system, according to the classification of schools located in differnet, differnet mission, teaching different functions, as well as regional and other characteristics of different regions, each school has a different more or less cabling place. However, there are several points which can be used as colleges campus cabling system to explore the commonalities, but also can be used as a variety of colleges and universities can learn from campus cabling system solutions.
1. Campus Cabling diversity
a. Building diversity
We also mentioned earlier, in the campus, especially college a wide variety of buildings, each building its building types and architectural features may vary. Some twenty or thirty or more layers of tall buildings (such as the school’s main building, complex building, etc.), while others are one, two dwarf room (such as canteens, etc.); Some large bay, less information building (such as school gymnasium, etc.); While others are small spaces, intensive information construction (such as multimedia classrooms or computer training room, etc.). For such floor height varies, of various sizes, the number of different information points, we have to make different plans. For high rise buildings, for the convenience and savings trunk cable laying wires, equipment room locationi will need to be carefully considered, such as computer room location is set to the middle of the building. And you do not need low building special consideration. For information point-intensive construction, telecommunications room on each floor of its location also needs attention. Because if you set reasonable, we can save a lot of horizontal cable; What’s more, if too much information points in the same layer, also need to consider setting up multiple telecommunications rooms. For large bays place, not only to consider the distribution of information points, but also consider wheter there is the level of information points length over 90 meters, if there are more than 90 meters of the situation, we need to consider the use of fiber optic cable or increase between telecommunications solutions. Also, in some campus gymnasium, auditorium and other places, also need to consider whether to set CP boxes and other issues.
b. Application of diversity
In colleges and universities, the diversity of buildings, each building determines the variety of applications. Such as teachers’ apartments, student dormitories, school comprehensive building, administration building, a variety of different teaching building, laboratory building used for research, data storage and computing centers. Applications and their information needs are very different. So many applications need not buildings and places, they must be designed according to different requirements. Teachers apartments, student dormitories according to ordinary residential buildings can be cabling design; househole classroom or every student dormitory apartment, basically meet a data point, a voice can be. Comprehensive building, administration building can be carried out according to the way commercial office planning and design; In addition to meet the demand of each office’s basic data, voice, consider increasing the internal campus network information in a specific department, such as education private network information point requirements. A variety of conferentce rooms, reception and other areas, need to consider adding wireless AP points. Data storage and computing centers can be designed according to the data center, to meet a variety of information throughout the campus switching, aggregation and storage. The experimental and research laboratory building as an important place, which may have strong radiation, corrosive material existence, there may exist high temperature, humidity, shock and vibration environments, there may be the most dangerous biological virus. Therefore, their application and requirements may be much more than we usually say ten categories of construction areas, so for special programs. To take into account not only the electromagnetic interference, environmental impact, but also consider the potential life safety issues. Therefore, these sites suggest using the whole screen or fiber class industrial grade high flame retardant wiring products, such as using fire-retardant grade reach CMP / OFNP grade, industrial grade reaches IP67 cabling products.
2. High-speed transmission of information
High speed transmission of information for campus cabling system is already a pressing task. A variety of multimedia transmission, video transmission and other large flow of data communication more and more. For school on the high speed network transmission channel is essential. Including multimedia educational system, remote network education system, digital libraries, data centers and other places, is information is very concentrated, at least to ensure Gigabit to the desktop, Gigabit backbone. Under the condition of the budget allows, it is best able to do Gigabit to the desktop, 40G/100G as the backbone for future development needs. For classroom apartment or student residence, it should try to make Gigabit to the desktop requirements. Because who knows, in the next 5-10 years, or longer period of time, how fast development of the Internet? telematics what would happen to the great changes? Campus Network what will change? So in product planning, to do not only meet the existing information and communication needs, but also to do with a certain forward looking.
3. Stability and security of information
In the campus network, the reliability and security of information transmission is very important, because it not only directly related to the use of campus communications network, but also to the entire campus of internal and external education system problems. Which may affect the security of network communications to the national education system. Instability in the event of information or information leaks, not only caused the affected education, and may bring significant social problems. Such as school entrance examination system due to system instability problems, or important information or test data within the education sector was stolen during transmission and so on. So campus intranet for information requirement is in any case have to ensure that the information transmitted high reliability, high security. In the planning and design of the campus cabling must be to choose a good quality cabling products, but also in fiber optic cabling system to avoid interference or disclosure of information. Achieve stable performance, reliable transmission of information security.
The Campus Cabling System Considerations
1. Disaster preparedness
Disaster prevention, for any cabling system is need, and also is necessary. On campus cabling system, pay attention to disaster prevention and many, such as earthquakes, lightning, flood, fire, etc. Around the school to the actual situation may have different, but in the integrated wiring system, the following two disasters have a very important relationship.
a. Lightning Stroke
Campus cabling system is different from general cabling system is one of the local architecture is numerous, wide distribution. Each building and interconnection of information between, or the information architecture and data center interconnection, must pass a variety of outdoor communication cables, so the campus backbone cable corresponding increase, which gives the outdoor cabling lightning protection challenges. Because once a root trunk cable struck by lightning, and the grounding system in case of a problem or did not do, when hundreds of thousands of volts high voltage transient will pass along the cables between devices, resulting in equipment damage, data lost, resulting in significant losses. So into the line of good grounding system and surge protection is very important. Of course, if you want to achieve more secure, avoid outdoor cables in danger of being struck by lightning can also be used outdoors in all non-metallic reinforcing
Outdoor Fiber Cable.
b. Fire Disaster
In addition to natural disasters, the current fire casualties and property loss is caused by the most serious disasters. On campus, most of the buildings are crowded places. In addition to selecting a variety of fire related materials and good fire prevention measures, cabling system cables fire retardant also has become essential. Because as the demand for information transmission, communications cable in the building has more than the number of number of strong electric cables trend, but the communication cable fire retardant has not been given due attention.
In addition, for campus cabling system, others, such as the computer room of the need to guard against seismic reinforcement, cables rat bite, etc., also need to pay attention.
2. Management
For school cabling systems, too much applications, and wide distribution of information points, application and needs vary, which brought the system management and maintenance of a great test. The traditional label drawing and handwriting management, or use the computer for documentation and preservation of the way, for such a large cabling systems, it has become beyond their grasp. In particular, to achieve a change to the information point and preservation of records in a timely manner, it is very difficult. Therefore, within the scope of the budget allows, it is recommended universities such as large scale cabling system uses intelligent infrastructure management system to improve cabling system maintenance and management, and enhance network security.
3. Intelligent Building digitized
In campus intelligent cabling, in addition to our previously mentioned, but also includes the campus radio systems, fire alarm systems, electronic fence system, monitoring system, LED large screen display systems, etc. These systems are in the transition to digital. Because of a digital campus will be teaching, research, management, technical services, services life and campus information collection, processing, integration, storage, transmission and application, so that the use of digital resources are fully optimized. By implementing from the environment (including equipment, classrooms, etc.), resources (such as books, handouts, courseware, etc.) to the application (including teaching, learning, management, service, office, etc.) all digitized, in the traditional campus built on a digital space to improve the operating efficiency of the traditional campus, expanding the traditional campus business functions, and ultimately the overall educational process information, so as to improve the management level and efficiency. Therefore, the campus all variety of intelligent system based on transmission channel will also jumped to Gigabit, and even Gigabit network requirements. In the design and planning, and perhaps to consider the application of digitization. In which the product can be selected copper Cat6a Cable, cat 6a, cat 7 products, fiber optic cable in OM3 Cable and other fiber optic products. However, for fire alarm systems, campus broadcasting system, and its products should be chosen to meet the high flame retardant properties, if possible, it is best to choose a high fire retardant cables. Because it does not lead to a fire occurs due to the rapid combustion of the cable causes the system to malfunction.
Figure 2: 305m Bulk Cat6 550MHz Cable UTP
Conclusion
Campus cabling system though complex, but as long as we grasp the core features of cabling system, clear the standard cabling system the basic requirements, specifically the various buildings, the application of the various systems and functions. It is not difficult to design and planning. Even the school have dozens, hundreds buildings, even if there are many school of information and communication applications, the final analysis are inseparable from the basic principles of cabling. Therefore, cabling system in the school, in order to maximize long as we grasp little less to more of the principles from the point to the line, from a line to a plane unfold. You will find, and then a big projects, the final show in front of us or our common and often do a single type of building cabling system, just follow their individual needs and applications for planning and design, you can complete set of perfect school cabling system.






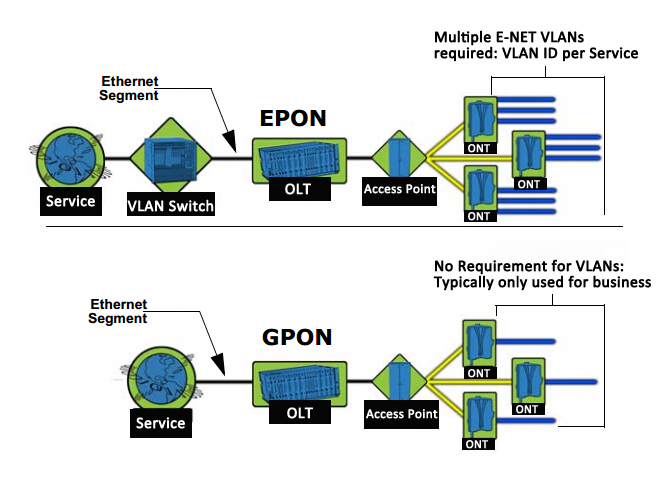

 Figure 1: Campus network design
Figure 1: Campus network design