Introduction
As all we known: cabling of building local area network (LAN) at the end of the 100m cabling, community area last 2km integrated network cabling computer data center room, such as several internal cabling. Cabling in different locations, in accordance with their purpose and corresponding transmission index calculating the length of the cabling to allow laying. No matter what position cabling used, all belong to the city telecommunications network extension and an important part. Only in depth understanding of urban development trends of telecommunication networks, in order to accurately grasp how to design integrated cabling; also only be taken with the city development strategy telecommunication network synchronization and with suitable, cabling can really play the overall effectiveness of the network and obtain win-win enconomic effects. Here only to the development of telecommunication networks, cabling should be synchronized with the development, as well as the latest developments in cabling issues such as study and discussion.
The development trend of telecommunication network
In traditional telecommunications networks based voice communication, a small amount of digital data network (DDN), Frame Relay (FR) point to point, such as low rate of data communication, a voice path begins only within the bandwidth of 64kbps. In the early 1990s, China’s foreign experience with the introduction of Ethernet Cable Wiring and network communication technology, and accordingly developed our standards, and actively promote the application of the telecommunications network to get great propress. In just 10 years time, network communication technology from 10 megabytes, 100 megabytes, Gigabit to 10 Gigabit-class development, or even 10 Gigabit-class network will soon put into large-scale application.
The development of the telecommunication network is omni-directional, methods of communication include: wired, wireless, satellite, etc.; Communication contents include: telephone, television, data, etc..
a. The rapid development of the passive optical network (PON)
Currently, the passive optical network (PON) is rapidly developing country, for example: EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network), GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network), GEPON (Gigabit Ethernet Passive Optical Network), APON (ATM Passive Optical Network), BPON (Broadband Passive Optical Network) and other network applications, structured cabling will have a direct impact. Now illustrate EPON/GPON networking mode:
EPON/GPON is mainly composed of OLT (Optical Line Terminal), ODN (Optical Distribution Network) and ONU (Optical Network Unit) and other components. EPON / GPON networking shown in Figure 1:
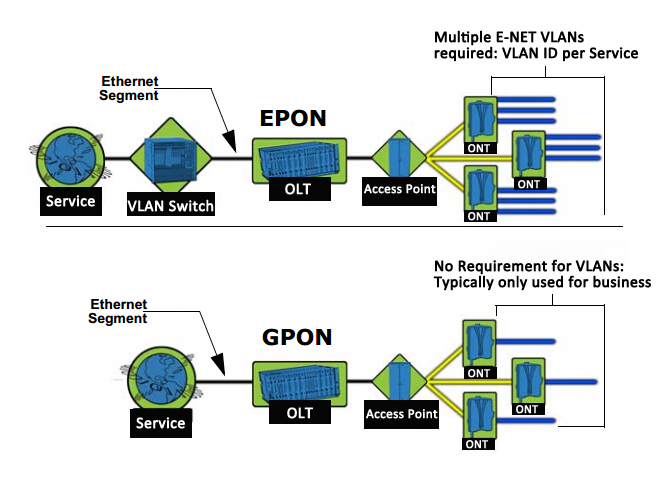
The network characteristics of EPON/GPON:
* On the OLT and ONU in addition to optical interface, combined with GE (Gigabit Ethernet), FE (Fiber optic Ethernet), RF (Radio Frequency), E1 (2.048Mbps) interfaces, can be applied to various network applications.
* EPON can provide uplink and downlink symmetrical rate 1.25Gbps.
* GPON can provides uplink 155Mbps, 622Mbps, 1.24Gbps or 2.48Gbps; Downlink 1.24Gbps or 2.48Gbps.
* Public IP network signal WDM CWDM DWDM, the uplink of 1490nm and downlink of 1310nm signal through the central office OLT integrated transceivers were injected into the same optical fiber, through the optical distribution network ODN spending 32.64 points or 128 optical link to the corresponding ONU. If necessary, can also be injected CATV signals using the third wavelength of 1550nm central office OLT transceiver integrated in the corresponding ONU than the client integrated transceivers separated by the RF interface of the user received a cable distribution network.
* EPON/GPON network support tree, star, bus, hybird and redundant topology etc..
* EPON is based on the standard Ethernet technology and IEEEP802.3ah, in the case of transport 1.25Gbps data stream, the optical line terminal (OLT) and the optical network terminal (ONU) between a transmission distance up to about 20km.
* GPON is based on the ITU-T standard G984.1-G984.5 version, is preferred in Europe and North America, FTTH technology, is being used worldwide. GPON generic framing protocol that provides a multi-protocol transmission efficiency can provide an open interface, with 2.48Gbps rate symmetric and asymmetric transmission capacity, OLT/ONU transmission distance up between 37km.
b. FTTH or FTTB/N
As EPON/GPON technology matures, the price of Optical Fiber Cable are more and more cheap. Fiber optic cable extends to the floor, community nodes, and even to the family increasingly likely. As telecom companies certainly want to consider the relationship between input and output in the short term cost recovery and profit is the ultimate goal.
The advantages of FTTH solutions:
1. Provide greater bandwidth capacity, suitable for high speed network applications.
2. Is not affected by the outside electromagnetic interference, anti-interference performance is good, high quality communications.
3. Silica fiber material production inexhaustible.
4. The price of fiber optic cable has lower than copper (but photoelectric conversion equipment price is still relatively high, therefore, the overall cost is higher).
The disadvantages of FTTH solutions:
1. Same scale projects, the initial investment is higher.
2. New fiber optic cable and more, longer construction period (relative to the FTTB/N solution).
3. Slow return on investment.
