In recent years, Cat6 data cabling has become more and more popular for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks. Recently, however, fiber optic cabling has become another popular way for businesses to maintain communications. So, as for Cat6 vs Fiber, which of these is best for your company? This article will show you how each works and what makes them different from one another.
Cat6 vs Fiber: What is Cat6 Cabling?
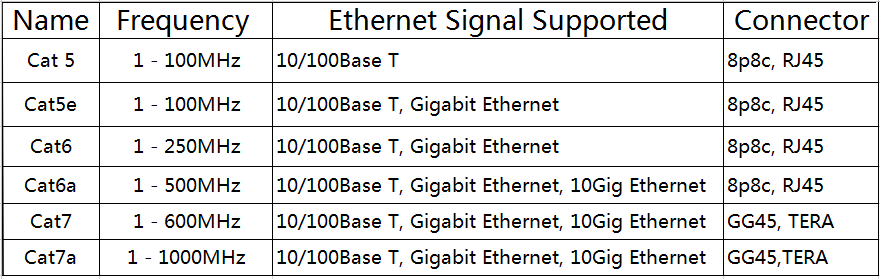
 Category 6 cabling (often shortened to cat-6 or cat6) is a type of data cabling that is standard for Gigabit Ethernet and several other network protocols which are not compatible with cat3 cables. As the sixth generation Ethernet cables formed from twisted pairs of copper wiring, cat6 is composed of four pairs of wires, similar to cat5 cables. The primary difference between the two, though, is that cable cat6 makes full use of all four pairs. This is why cat6 cable can support communications at more than twice the speed of Cat5e patch panel, allowing for Gigabit Ethernet speeds of up to 1 gigabit per second.
Category 6 cabling (often shortened to cat-6 or cat6) is a type of data cabling that is standard for Gigabit Ethernet and several other network protocols which are not compatible with cat3 cables. As the sixth generation Ethernet cables formed from twisted pairs of copper wiring, cat6 is composed of four pairs of wires, similar to cat5 cables. The primary difference between the two, though, is that cable cat6 makes full use of all four pairs. This is why cat6 cable can support communications at more than twice the speed of Cat5e patch panel, allowing for Gigabit Ethernet speeds of up to 1 gigabit per second.
It is cat6’s speed that has made it such a great choice for VoIP telephony, but there are some setbacks. For starters, there are length restrictions in using this type of data cabling. When used for 10/100/1000BASE-T, the restriction is 100 meters, and when used for 10GBASE-T, the restriction is 55 meters. Another issue is that there are some cat6 cables that are very large and are quite difficult to connect to 8P8C connectors (a type of modular connector used for communications purposes such as phone/Ethernet jacks) when the user does not have a unique modular piece.
Cat6 vs Fiber: What about Fiber Optic Cabling?
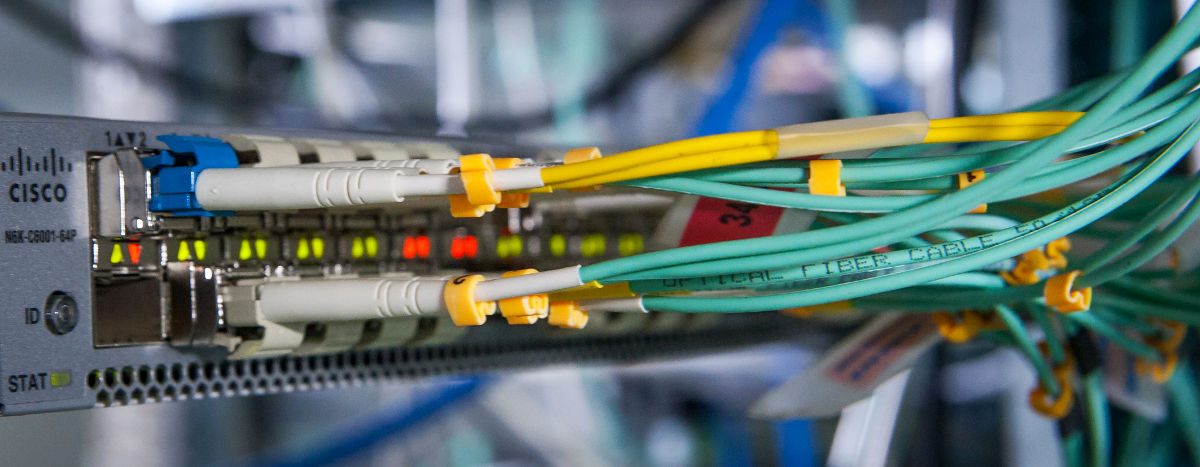
Fiber optic cabling sometimes referred to as optical fiber, which is completely different from cat6 and other types of structured cabling systems. This is because optical fiber works by drawing on light as opposed to electricity as a means of transmitting signals. As we all know, light is the fastest mode of transmitting any information which is great for businesses with the need for speed. And because fiber optic cabling has a much cleaner signal than conventional copper cabling, it is able to transmit signals faster than ever before.
Another great thing about optical fiber is that it is immune to electrical interference. This means that a user can run it just about anywhere, anytime. The immunity of light to resistance also allows fiber optic cabling to be run over extremely long distances. In fact, it can be run countries apart without any need for boosting or cleaning the signal.
Cat6 vs Fiber: Which Should You Choose?
If you prefer to stick with old and reliable, copper data cabling may be your best option for now. But be aware that soon, fiber optic cabling may be the only option as it grows in popularity. If you prefer higher speeds, you may want to switch to fiber optic cabling right now—it’s getting faster and better every day. Fiberstore offers both Cat6 copper cables and all kinds of fiber optic patch cable with different connectors. Wish it may satisfy your needs!
Related Article:
Difference Between Fiber Optic Cable, Twisted Pair Cable, and Coaxial Cable
Running 10GBASE-T Over Cat6 vs Cat6a vs Cat7 Cabling?
Choose 10GBASE-T Copper Over SFP+ for 10G Ethernet
Will Copper Cables Still Be an Indispensable Part in Data Center?