Fiber optic cables transmit data through very small cores at the speed of light. Significantly different from copper cables, fiber optic cables offer high bandwidths and low losses with the help of the core and cladding. And it allows high data-transmission rates over long distances. Light propagates throughout the fiber cables according to the principle of total internal reflection.
There are three common types of fiber optic cables: single-mode, multimode, and graded-index. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. There also are several different designs of fiber optic cables, each made for different applications. In addition, new fiber optic cables with different core and cladding designs have been emerging; these are faster and can carry more modes. While fiber optic cable are used mostly in communication systems, they also have established medical, military, scanning, imaging, and sensing applications. They are also used in optical fiber devices and fiber optic lighting.
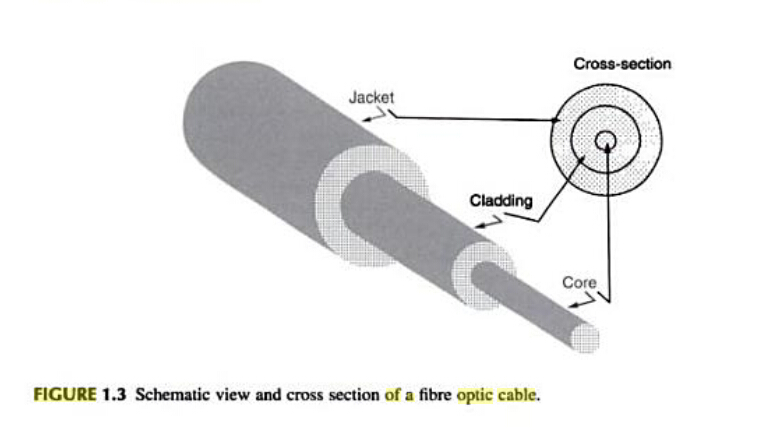
Fiber optic cable is a filament of transparent material used to transmit light, as shown in Figure 1.2. Virtually all fiber optic cables share the same fundamental structure. The centre of the cable is referred to as the core. It has a highter refractive index than the cladding, which surrounds the core. The contact surface between the core and the cladding creates an interface surface that guides the light; the difference between the refractive index of the core and cladding is what causes the mirror like interface surface, which guides light along the core. Light bounces through the core from one end to the other according to the principle of total internal reflection, as explained by the laws of light. The cladding is then covered with a protective plastic or PVC jacket. The diameters of the core,cladding, and jacket can vary widely; for a single fiber optic cable can have core, cladding, and jacket diameters of 9, 125, and 250 um, respectively.
Figure 1.3 shows the structure of a typical fiber optic cable. The cores of most fiber optic cables are made from pure glass, while the cladding are made from less pure glass. Glass fiber optic cable has the lowest attenuation over long distances but comes at the highest cost. A pure glass fiber optic cable has a glass cladding. Fiber optic cable core and cladding may be made from plastic, which is not as clear as glass but is more flexible and easier to handle. Compared with other fiber cables, Plastic Optical Fiber Cable is limited in power loss and bandwidth. However, they are more affordable, easy to use, and attractive in applications where high bandwidth or low loss is not a concern. A few glass fiber cable cores are clad with plastic. Their performance, though not as good as all-glass fiber cables, is quite respectable.
The jacket is made from polymmer (PVC, plastic, etc.) to protect the core and the cladding from mechanical damage. The jackets has several major attributes, including bending ability, abrasion resistance, static fatigue protection, toughness, moisture resistance, and the ability to be stripped. Fiber optic cable jackets are made in different colours for colour-coding identification. Some optical fibers are coated with a copper-based alloy that allows operation at up to 700 and 500℃ for short and long periods, respectively.
Fiberstore is a leading supplier of Fiber Optic Cable and components into the umbilical and towed array products for the oil & gas sector. The key technology for these products is Fiberstore’s patented stainless steel fiber optic tube technology which packages the optical fiber in the best possible way resulting in a robust, compact product that is suitable for the high pressure of the subsea environment. Fiberstore will customize the design to meet your needs to include different fiber counts, fiber types, metal types, tube sizes, belting materials, armor type, armor size, armor count, encapsulation types, color, print, packaging and length.
Related Article: Which Patch Cable Should I Choose for My Optical Transceiver?
Related Article: The Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber