Nowadays networks are carrying significant volumes of data at increasing speeds – it is getting more complex than ever. Consequently, network visibility is critical to monitor, manage and protect your network. So having access to inner working condition of the network is paramount to every network manager. Network TAP and network switch port mirroring provide direct access to the actual packets navigating across networks. If both options work, which is a better choice? And when should we choose one over the other? We try to address those issues here.
Basics of Network Switch Port Mirroring
Network switch port mirroring is nothing new for us. It is performed by a mirror port – a software feature built into a network switch that creates a copy of selected packets passing through the device and sends them to a designated mirror port. It enables a network manager to configure or change the data to be monitored. Since the primary purpose of a network switch is to forward production packets, port mirroring data is often with a lower priority. Besides, switch port mirroring uses a single egress port to aggregate multiple links, so it is easily oversubscribed.
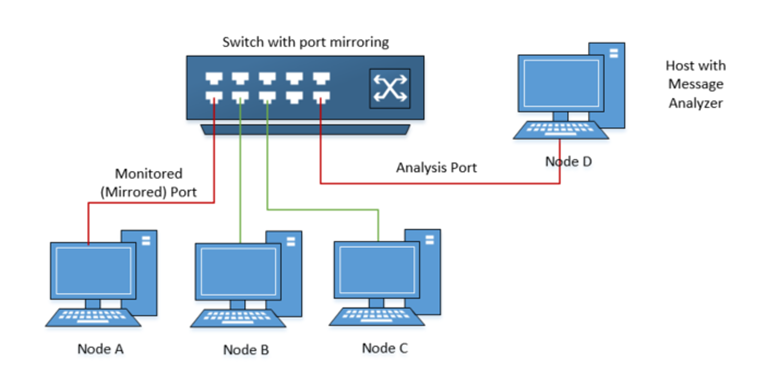
- Low cost, using existing switch capabilities.
- Remotely configurable through the network.
- Captures intraswitch traffic.
- Drops packets on heavily used full-duplex links.
- Filters out Physical Layer errors.
- May burden the switch’s CPU to copy data.
- May change frame timing, altering response times and slowing network performance.
Network TAP Explanation
A network TAP (Test Access Point) is a passive device that used to directly connect to the cabling infrastructure. Instead of two switches or routers connecting directly to each other, the network TAP is put between the two devices and all data flows through the TAP. With an internal splitter, the TAP creates a copy of the data for monitoring while the original data continues unimpeded through the network. In this case, packet of any size can be copied by TAP – it thus eliminates any chance of oversubscription. Once the data is TAPed, the duplicate copy can be used for any sort of monitoring, security, or analytical use.
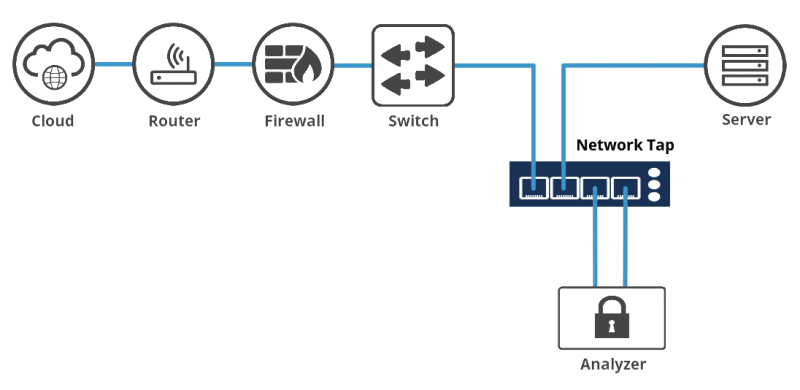
- Captures send and receive data streams simultaneously, eliminating the risk of dropped packets.
- Provides full visibility into full-duplex networks.
- Captures everything on the wire—including Physical Layer errors—even when the network is saturated.
- Requires the purchase and installation of additional hardware.
- Analysis device may need dual-receive capture interface.
- Only captures data between network devices; can’t monitor intra-switch traffic.
Network TAP vs Switch Port Mirroring: Differences?
The differences concerning port mirroring and network TAP is summarized as following.
- TAPs create an exact copy of the bi-directional network traffic at full line rate, providing full fidelity for network monitoring, analytics and security. While network switch mirror ports are easily oversubscribed – resulting in dropped packets, which leads to inconsistent results for monitoring and security purposes.
- Passive TAPs provide continuous access to traffic and require no user intervention or configuration once installed. Network switch port mirroring, however, can have a negative performance impact on the switch itself, sometimes affecting network traffic.
- Network TAPs allow for traffic monitoring for a particular segment. But port monitoring traffic output can change from day to day or hour to hour – resulting in inconsistent reporting. When configured mirror ports incorrectly, it will impact network performance.
- TAPs are usually protocol transparent – be it carried in the traffic or if it is IPv4 or IPv6. All traffic is passed through a passive TAP.
- Network switch mirror ports are limited in number compared to the number of ports that may require monitoring, and consume ports that could otherwise be carrying production traffic.
Network TAP vs Port Mirroring: When to Use Which?
Simply put it, TAPs are a key component and should be applied in any system demanding 100% visibility and traffic fidelity. And whenever traffic volumes are moderate to high, it’s better to deploy network TAPs. Note that inserting a TAP into an existing network link requires a brief cable disconnect, so TAPs are typically installed during a maintenance window, or to install it during the early design phase.
On the other hand, network switch port mirroring works best for ad hoc monitoring of low volumes of data in locations where TAPs have not been installed. It still represent the only means for accessing certain types of data, such as data crossing port-to-port on the same switch, remote locations with modest traffic that cannot justify a fulltime TAP, or traffic that stays within a switch that never reaches a physical link.
Conclusion
There is no doubt that both TAPs and network switch mirror ports can provide valid access to data if used correctly. Choose network TAP when you can justify the cost, while opt for port mirroring where you must. FS.COM is backed by a professional and experienced team to provide solutions for network TAPs and Ethernet switch, for more details, feel free to contact us via sales@fs.com.
Related Article: TAP Aggregation: A Key Monitoring Tool for Network