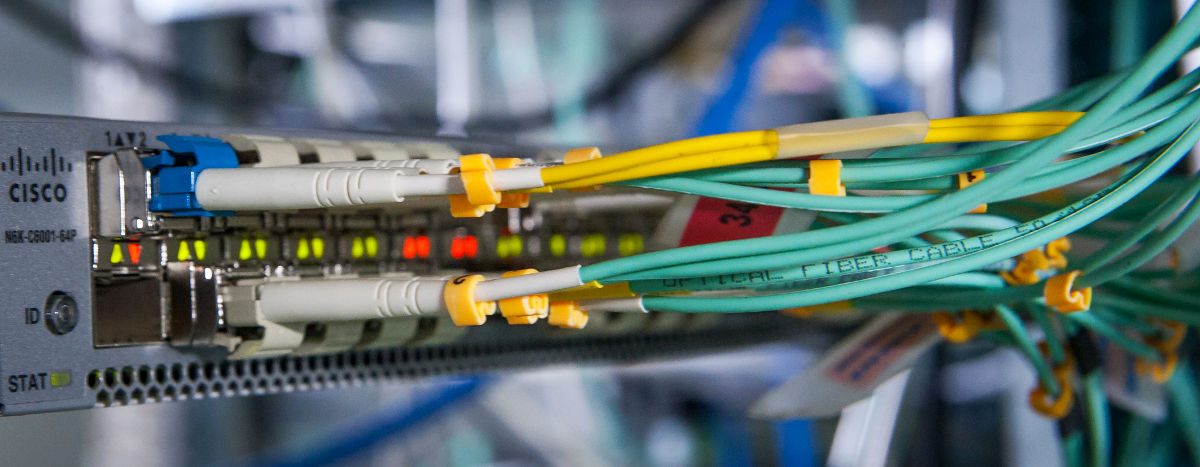
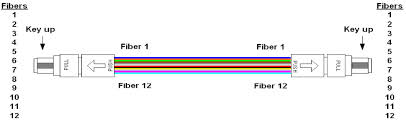
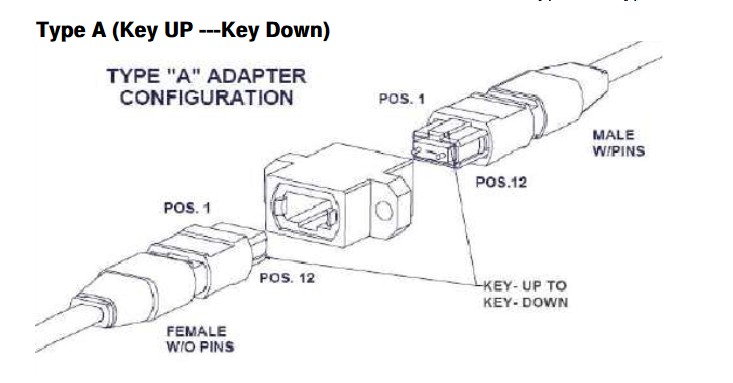
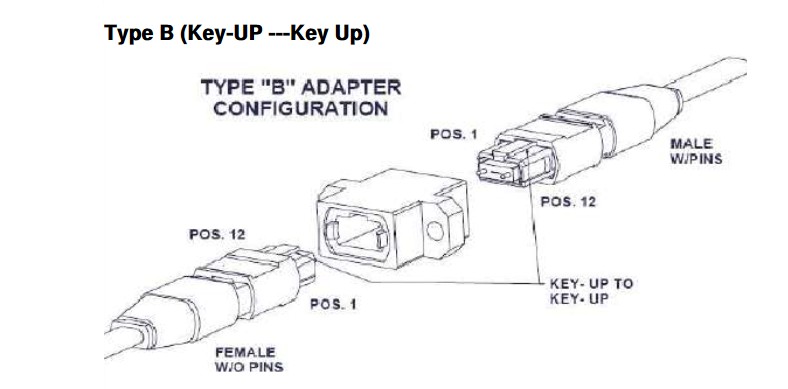
Ribbon cables terminated with MPO connetors present some challenges when it comes to maintaining the correct signal crosssover in a segment consisting of multipe fiber optic srands. The ANSI/TIA-568-C.3 standard provies a set of “Guidelines for Maintaing Polarity Using Array Connetors” that decribe three types of MPO-to-MPO array cables, defined as Types A, B, and C. These cables are used to provide three different methods for maintaining a crossover connection. Method A is prefferred method, and is based on Type A MPO Fiber cables.
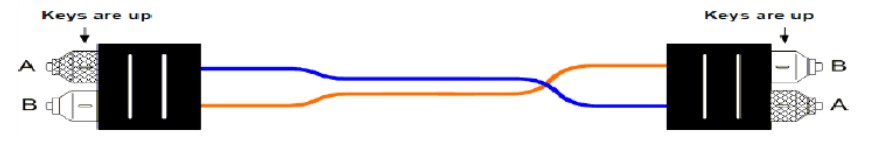
Figure 17-6 shows a Type A straight through ribbon cable with 12 fibers terminated in MPO connetor. A Method A backbone link is cabled “straight through”, terminating in the cabling system patch panel. One end of the link will have a straight through patch cable, connetion from the patch panel to the Ethernet interface. The other end of the link will have a crossover cable connecting to the Ethernet interface. The guidelines recommend keeping all of the crossover patch cables at one end of the link, to keep the system as simple as possible and help the installer to avoid connecting the wrong type of patch cale.
The guidelines also show Method B and Method C, which are two methods for providing a crossover patch built into the MPO backbone cables themselves. Given the complexity of these approaches and the difficulty of implementing them correctly, they are both rarely used.
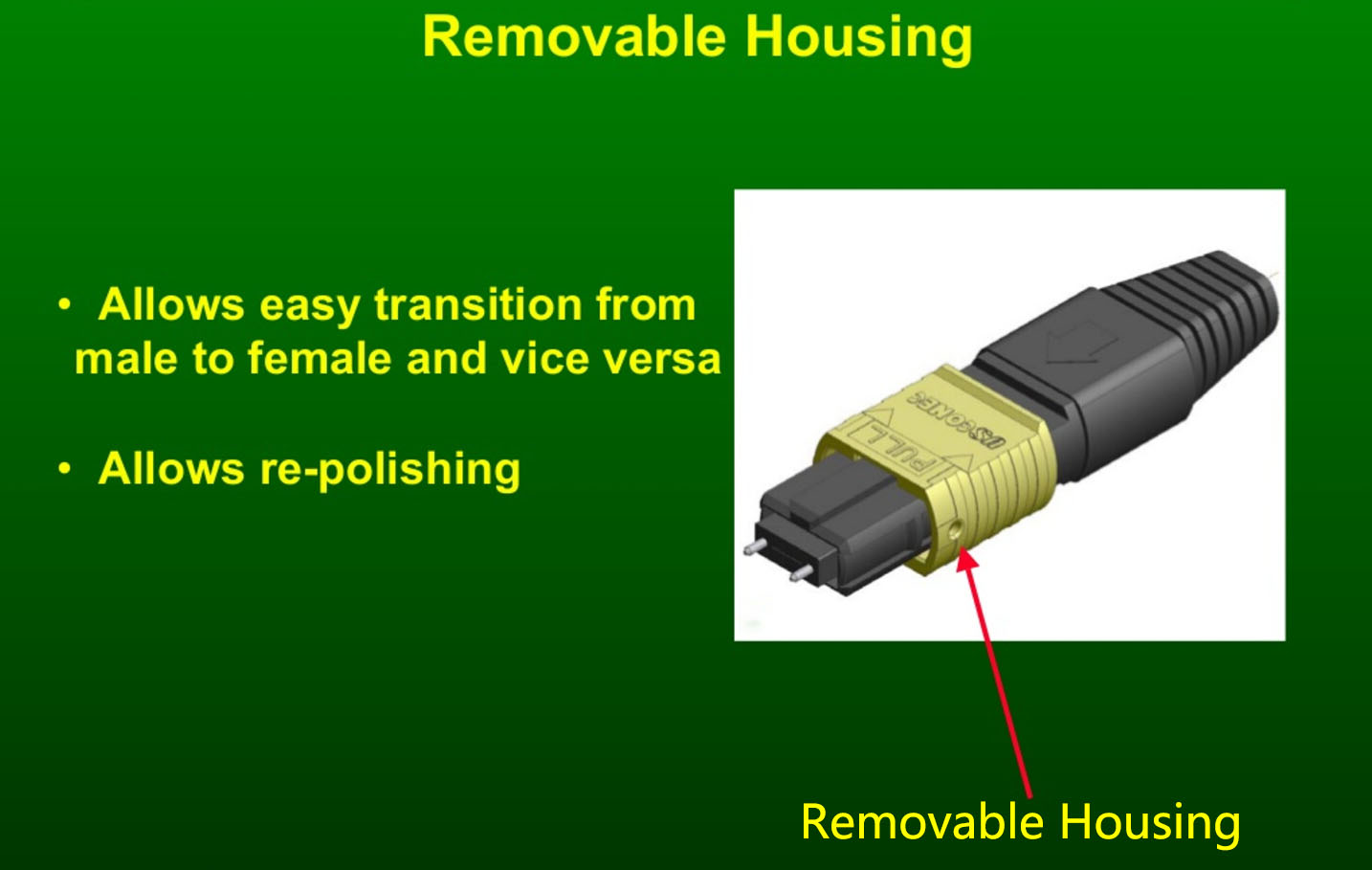
As you can see, there are a variety of approaches to managing the signal crossover for the 12-fiber and 24-fiber systems needed to support 40 and 100 Gb/s Ethernet. For the best results, make sure you know which method your site is using in the cabling system, and order the correct MPO cable types to make the connections and achieve the signal crossover. Note that some vendors provide special MPO connectors that make it possible to change connector gender and polarity(crossover) in the field, which coulde be a handy way to resolve MPO-to-MPO connectivity issues.
To provide an introduction and basic information to readers, this section begins with a presentation of the components needed for a parallel optical MPO connection.
MPO connectors contact up to 24 fibers in a single connection. A connection must be stable and its ends correctly aligned. These aspects are essential for achieving the required transmission parameters. A defec-tive connection may even damage components and or cause the link to fail altogether.
MPO cables are delivered already terminated. This approach requires greater care in planning in advance but has a number of advantages: shorter installation times, tested and guaranteed quality and greater reli-ability.
Fiber trunk cables serve as a permanent link connecting the MPO modules to each other. Trunk cables are available with 12, 24, 48 and 72 fibers. Their ends are terminated with the customer’s choice of 12-fiber or 24-fiber MPO connectors.
Harness cables provide a transition from multi-fiber cables to individual fibers or duplex connectors.The 12-fiber harness cables available from R&M are terminated with male or female connectors on the MPO side, the whips are available with LC or SC connectors.
Fiberstore supply MTP MPO fiber cables, MTP Cassette and MPO Cassette. MTP MPO cables are available in 4,8,12, 24, and 48 fiber array configurations. Many additional options and combinations are available. All fiber optic cables are customizable.