Nowadays, Ethernet switch has become an important part in data center or computer networking to meet different needs. You may heard about it but not so familiar with it. Then, what is an Ethernet switch? How does an Ethernet switch work? Let’s find out the answers in the following text.
What Is an Ethernet Switch?
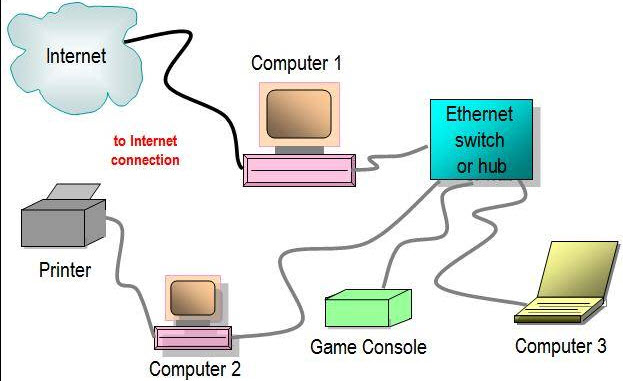
Ethernet switch, the most common form of network switch, is a computer networking device used in Ethernet to connect various Ethernet devices. It connects devices together by using packet switching to receive, process, and forward data from one source device to another destination device.
There are various types of Ethernet switches designed for different needs. Normally, they are divided into two main categories, namely, modular switch and fixed configuration switch. The former one allows you to add expansion modules into the switch as needed while the latter one is not expandable with a fixed number of ports.
Nowadays, fixed configuration switches are the mostly used. They can come in various different speeds with particular names such as fast Ethernet switch with a speed of 10/100 Mbps, Gigabit Ethernet switch of 10/100/1000 Mbps, 10GbE switch of 10/100/1000/10000 Mbps. Currently, Gigabit Ethernet switch is still the most common one and is the most widely used switch among its kind. In additional, 10GbE switch is also very popular for its higher transmission speed of up to 10 Gbps and a relatively not expensive price. Of course, there are other switches of 25G, 40G or even 100G for you to choose as well. You can choose the best Ethernet switch according to your actual needs.
How Does An Ethernet Switch Work?
As a hardware device, Ethernet switch centralizes communications among multiple connected Ethernet devices in one local area network (LAN). Normally, multiple data cables are plugged into an Ethernet switch to enable communication between different networked devices. Then, the Ethernet Switch manages the flow of data across the network by transmitting a received network packet only to the one or more devices for which the packet is intended. An Ethernet switch can identify every device connected to it and direct the traffic flow of the device, which maximizes the security and efficiency of the network. Therefore, it is more intelligent and efficient than an Ethernet hub which is unable to distinguish different recipients.
How to Choose and Use an Ethernet Switch?
As for how to choose an Ethernet switch, there are different factors you should consider:
- Transmission speed: Although there are different transmission speeds for you to choose, you still need to use an Ethernet switch according to the actual speed you need.
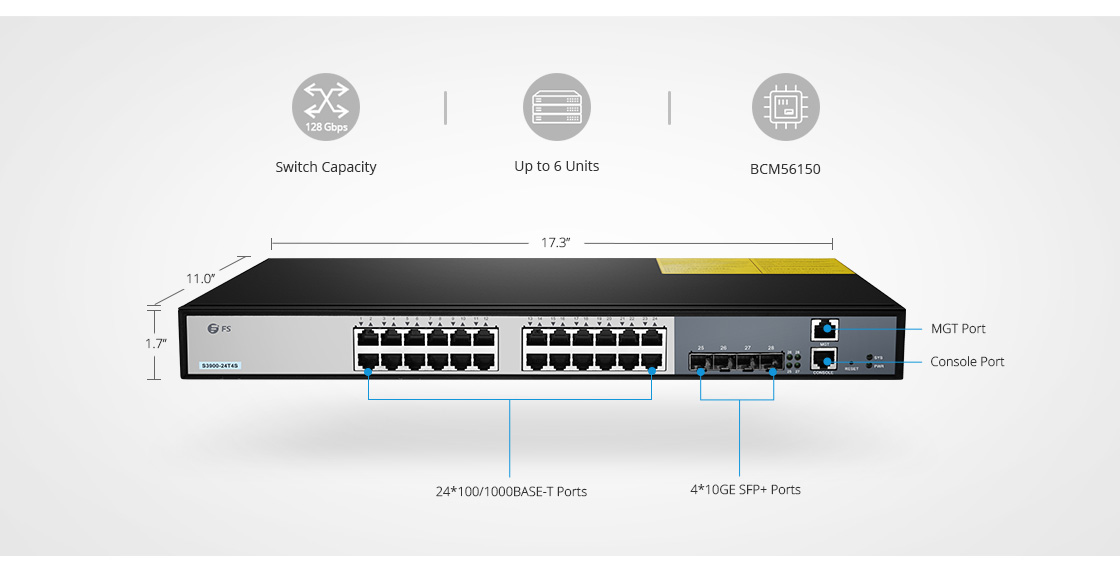
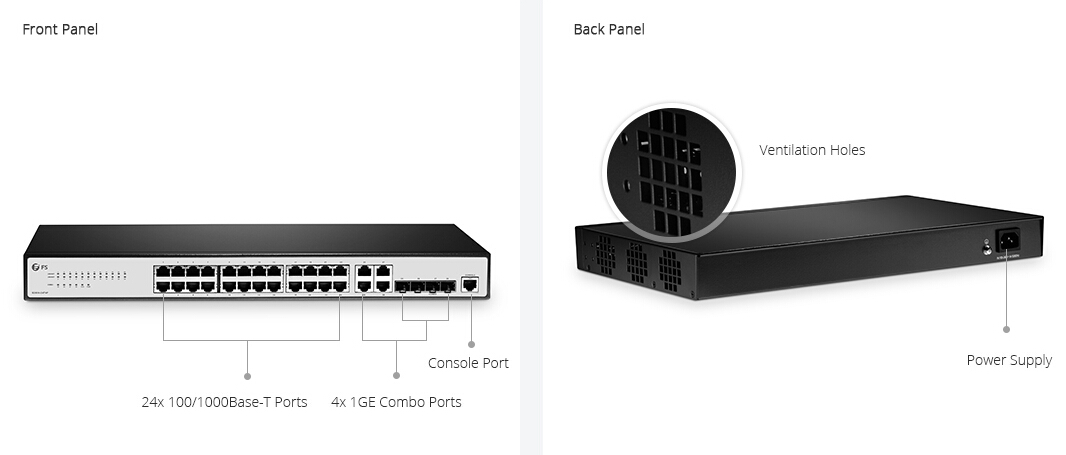
- Number of ports: Fixed configuration switches typically come in 5, 8, 10, 16, 24, 28, 48, and 54-port configurations. You should choose a switch with the number of ports equal to, or greater than that of computers you are connecting.
- Network infrastructure: For small network of up to 50 users, one Ethernet switch might enough. While, additional switches are needed if more users are added in.
- Specific feature: If you have special requirements for your switch, you can search it accurately. For example, you can only search managed or unmanaged switch for precise localization among various switches.
- Reliable vendor: There are many popular brands of networking equipment, such as Cisco, 3com, Linksys, FS, etc. Just choose a company you trust and buy the switch you want.
- Price difference: Normally, price might be the priority over everything when choosing a product. You can search a certain switch of the same external conditions and then compare them in price. If the functions are nearly the same, you can choose a relatively cheaper one.
Speaking of how to use an Ethernet switch, you can follow the guidance below:
- Configure your switch: Set up the IP address for the switch with switch manual.
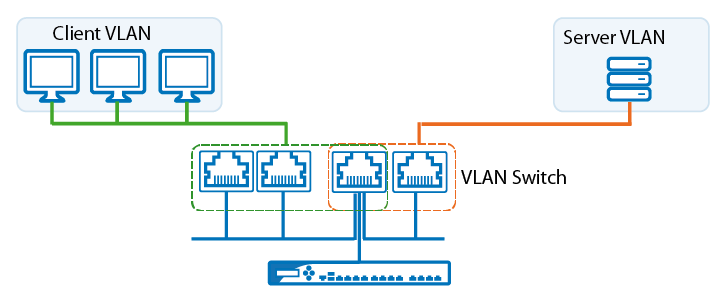
- Configure your switch with right VLANs setup if needed. If multiple VLANs are being used, make sure the computers are on the correct VLAN.
- Log into your switch to hard code each port if necessary.
For more details, you can refer to the post of how to use a network switch.
Conclusion
After the introduction of “What is an Ethernet switch?” and “How does an Ethernet switch work?” above, one can have a general understanding of an Ethernet switch. In short, An Ethernet switch is a telecommunication device used to connect multiple computers or devices together and can expand network with ease.
Switch Mac Address: What’s It and How Does it Work?