As data communications technology migrates from 10GbE to 40GbE and beyond, it is often necessary to connect 40GbE equipment with existing 10GbE equipment. As we know 40GbE NIC or switch usually equipped with QSFP+ ports, and 10GbE switch usually equipped with SFP+ ports. That is to say we must know how to convert a QSFP+ port to a SFP+ port. At present, there exists three ways to solve this problem. I will explain it in this blog.
QSFP+ to SFP+ Cable
As shown in the figure below, a QSFP+ to SFP+ cable consists of a QSFP+ transceiver on one end and four SFP+ transceivers on the other end. The QSFP+ transceiver connects directly into the QSFP+ access port on the switch. The cables use high-performance integrated duplex serial data links for bidirectional communication on four links simultaneously. The SFP+ links are designed for data rates up to 10 Gbps each. QSFP+ cable is available in passive and active two types. Passive QSFP+ cable has no signal amplification built into the cable assembly, therefore, their transmission distance is usually shorter than an active one.

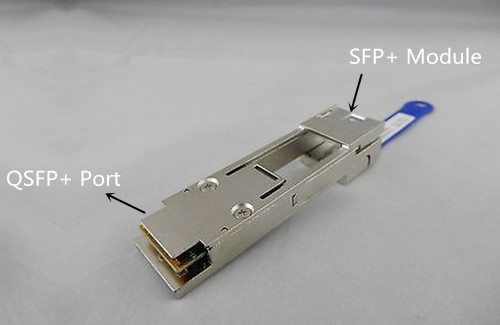
CVR-QSFP-SFP10G: QSFP+ to SFP+ Adapter (QSA)
You can convert a QSFP+ port to a SFP+ port using the QSFP+ to SFP+ adapter. QSA provides smooth connectivity between devices that use 40G QSFP+ ports and 10G SFP+ ports. Using this adapter, you can effectively use a QSFP+ module to connect to a lower-end switch or server that uses a SFP+ based module. This adapter is very easy to use. As shown in the figure below, just plug one side of the QSA in your QSFP+ port, and plug a SFP+ module into another side of the QSA. Then you can convert a QSFP+ port to a SFP+ port easily.
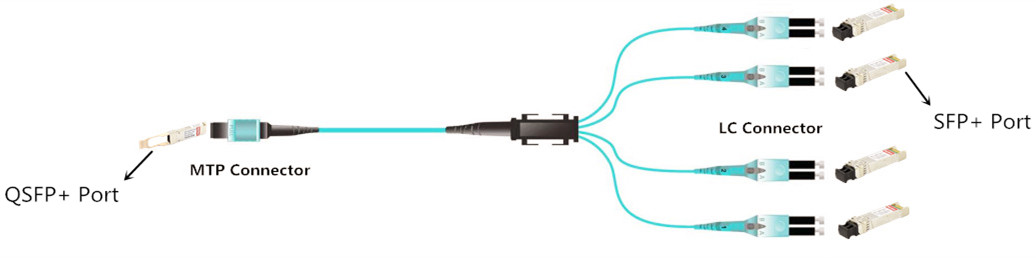
QSFP+ Breakout Cable
As we know, parallel 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ modules use 8 out of 12 MPO/MTP interface fibers transmitting 4 x duplex (DX) channels (4 x transmit and 4 x receive). The QSFP+ breakout cable uses a pinless MTP connector on one end for interfacing with the QSFP port on the switch. The other end contains 4 duplex LC connectors, which provide connectivity to the SFP+ ports on the switch. Thus higher-speed equipment (40G QSFP+) can be connected to slower-speed equipment (10G SFP+) successfully.
Conclusion
When you want to connect a QSFP+ port to a SFP+ port, you can use QSFP+ to SFP+ cable, QSFP+ to SFP+ adapter or QSFP+ breakout cable. All these three options can meet your needs. FS.COM provides a full range of compatible QSFP+ cable, which can be 100% compatible with your Cisco, Juniper, Arista and Brocade switches and routers. Or you want to use QSFP+ breakout cable, you can also find it in our Fiberstore.
Related Article: 10G SFP+ and 40G QSFP+ Transceivers Cabling Solutions





 The 40GBASE-LR4 CWDM QSFP+ transceiver, such as
The 40GBASE-LR4 CWDM QSFP+ transceiver, such as 
 Unlike CWDM QSFP+ transceiver which uses a LC connector, PSM QSFP+ is a parallel single-mode optical transceiver with an MTP/MPO fiber ribbon connector. It also offers 4 independent transmit and receive channels, each capable of 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G on 10km of single-mode fiber. Proper alignment is ensured by the guide pins inside the receptacle. The cable usually cannot be twisted for proper channel to channel alignment. In terms of a PSM QSFP+, the transmitter module accepts electrical input signals compatible with common mode logic (CML) levels. All input data signals are differential and internally terminated. The receiver module converts parallel optical input signals via a photo detector array into parallel electrical output signals. The receiver module outputs electrical signals are also voltage compatible with CML levels. All data signals are differential and support a data rates up to 10.3G per channel.
Unlike CWDM QSFP+ transceiver which uses a LC connector, PSM QSFP+ is a parallel single-mode optical transceiver with an MTP/MPO fiber ribbon connector. It also offers 4 independent transmit and receive channels, each capable of 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G on 10km of single-mode fiber. Proper alignment is ensured by the guide pins inside the receptacle. The cable usually cannot be twisted for proper channel to channel alignment. In terms of a PSM QSFP+, the transmitter module accepts electrical input signals compatible with common mode logic (CML) levels. All input data signals are differential and internally terminated. The receiver module converts parallel optical input signals via a photo detector array into parallel electrical output signals. The receiver module outputs electrical signals are also voltage compatible with CML levels. All data signals are differential and support a data rates up to 10.3G per channel.