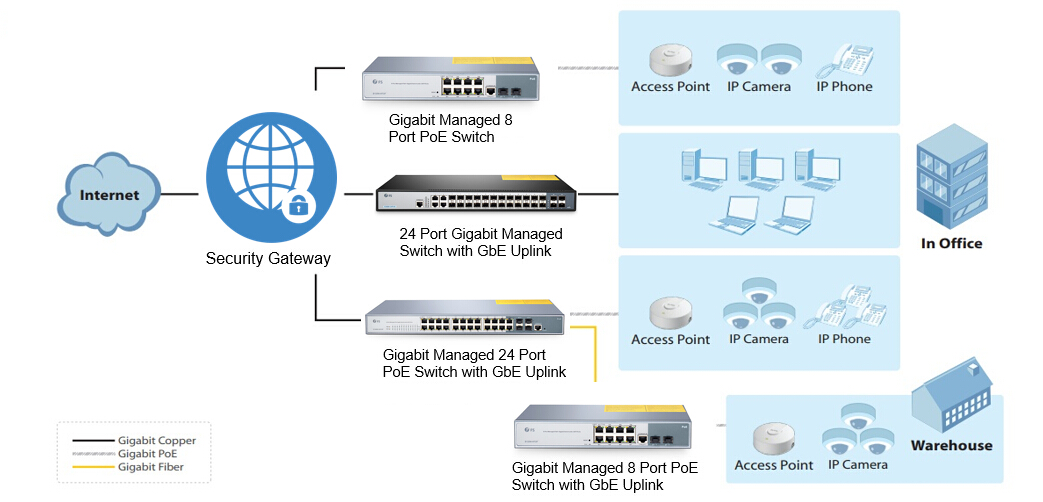
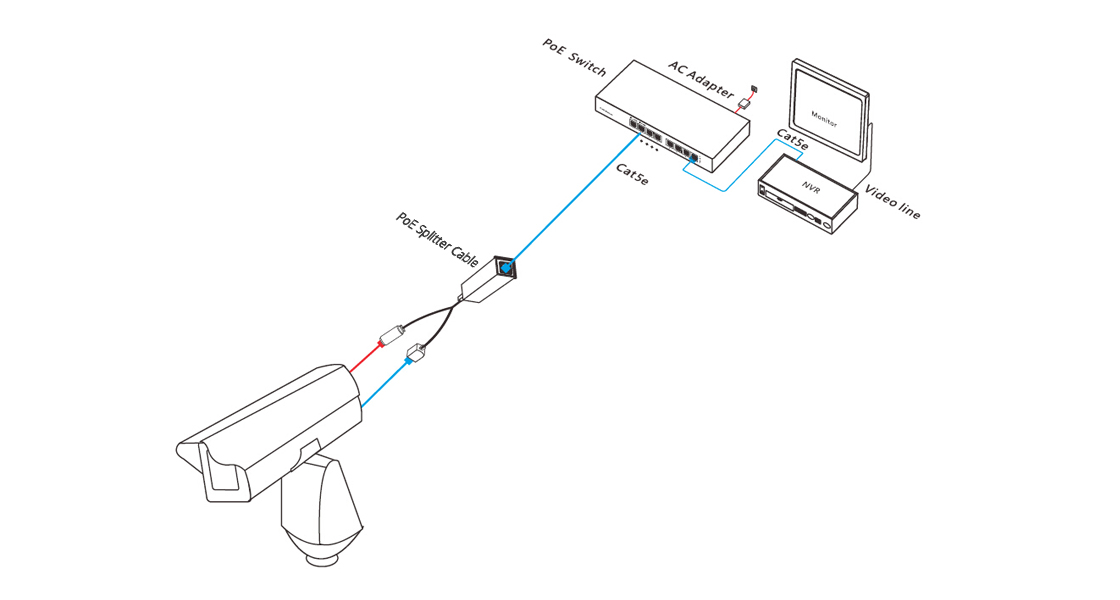
Network switch is the major building block of many business networks, as they connect multiple PCs, printers, access points, servers, and other hardware to make your business up and running. Switches enables you to send and receive information and access shared resources in a smooth, efficient and highly secure way. It happens at some points we need to make settings or adjustments on switches to perform certain function, like configuring VLAN or check status of switch ports. So how to get the configuration access to a network switch? Does GUI or CLI work better for you? What’s the difference between GUI vs CLI? We’ll address these issues and guide you to manage switch via GUI and CLI.
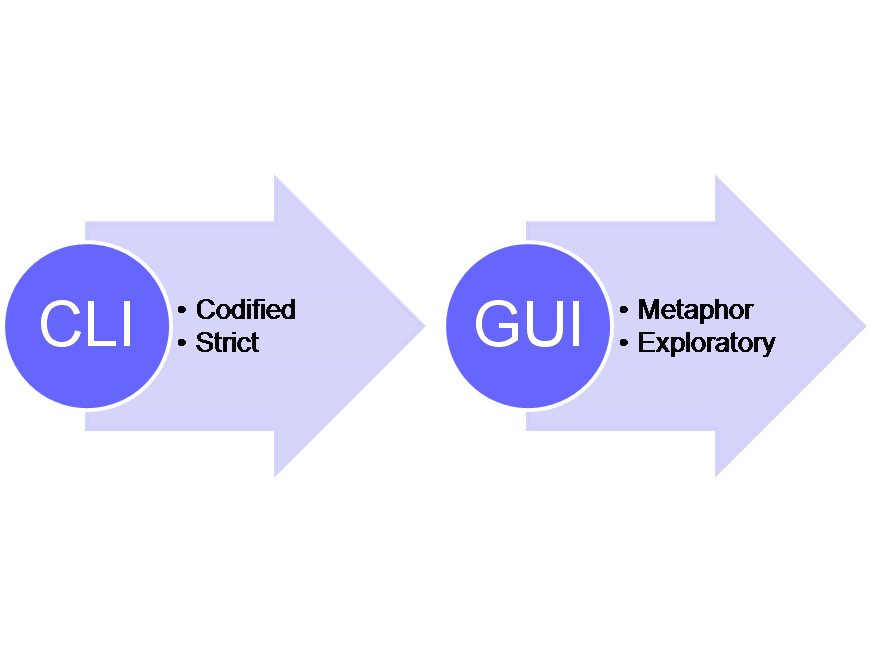
What Is GUI (Graphical User Interface)?
GUI is short for Graphical User Interface – it uses graphics like windows, scrollbars, buttons, etc. to allow users to communicate with the data switch or GUI operating system. It facilitate users, especially novice users in an intuitive and easy-to-learn way. GUI access need recognition and good exploratory analysis and graphics, which is more suitable for users who requires no access to advanced tasks.
What Is CLI (Command Line Interface)?
CLI stands for Command Line Interface, which allows users to write commands in a terminal or console window to communicate with an operating system. CLI acts as the medium between operators and the network switch: Users have to type command to perform a task. CLI is more accurate than GUI, but it has a very steep learning curve. CLI is appropriate for users who uses it in a regular basis, or for the costly computing where input precision is the priority.
GUI vs CLI: What Is the Difference?
GUI vs CLI, both as the mainstream interface for accessing network switch, differs in the following aspects:
Ease of Use: CLI enable users to type manual command in order to perform the desired task whereas in GUI users provided visuals to communicate with the data switch. So the beginners will pick up a GUI much faster than a CLI.
Control: With a GUI, there’s control over files and the operating system – but advanced tasks may still need CLI. While CLI enables all the control over file system and operating system, making tasks simple.
Speed: In GUI, using the mouse and the keyboard to control is slower than using the command line. With CLI, the operator simply use the keyboard and may need to execute only few commands to complete the task.
Hacking: In terms of hacking, all the vulnerability exploits are done from command line. All the remote access and file manipulation are done from the command line.
Scripting: CLI excels in this field since it allows you to create a script that contains few lines of command and it will do the work for you.
Here we use the chart to summarize GUI vs CLI differences.
|
BASIS FOR COMPARISON
|
CLI
|
GUI
|
|
Basic
|
Command line interface enables a user to communicate with the system through commands.
|
Graphical User interface permits a user to interact with the system by using graphics which includes images, icons, etc.
|
|
Device used
|
Keyboard
|
Mouse and keyboard
|
|
Ease of performing tasks
|
Hard to perform an operation and require expertise.
|
Easy to perform tasks and does not require expertise.
|
|
Precision
|
High
|
Low
|
|
Flexibility
|
Intransigent
|
More flexible
|
|
Memory consumption
|
Low
|
High
|
|
Appearance
|
Can’t be changed
|
Custom changes can be employed
|
|
Speed
|
Fast
|
Slow
|
|
Integration and extensibility
|
Scope of potential improvements
|
Bounded
|
GUI vs CLI: How to Use Them to Manage Network Switch?
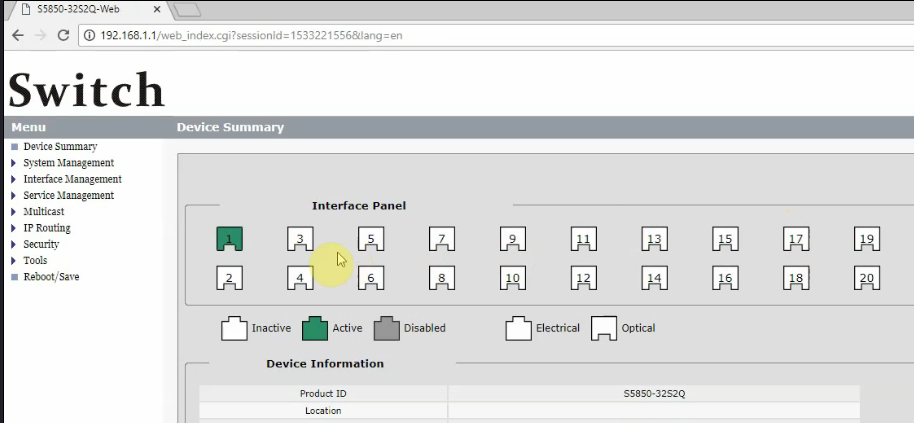
CLI and GUI are different kinds of user interfaces with their own merits and drawbacks. It is important to understand where each one excels so you can pick the right tool. Using the defining features of two different tools provides the best of both worlds. The following video, using FS S5850-32S2Q 10GbE switch as an example, offers a complete guide on how to use command line and GUI to access a network switch, through which you may figure out which one fits better for you.
Conclusion
In all, the GUI provides a higher degree of multitasking and more efficiency, whereas CLI offers more control, precision and repeatability. The decision on choosing GUI vs CLI to configure the network switch should better based on user requirements. FS.COM offers a comprehensive product line of network switches, including Gigabit Ethernet switch, Gigabit PoE switch, etc. If you are seeking network switch configuration or management solutions, feel free to contact us at sales@fas.com.