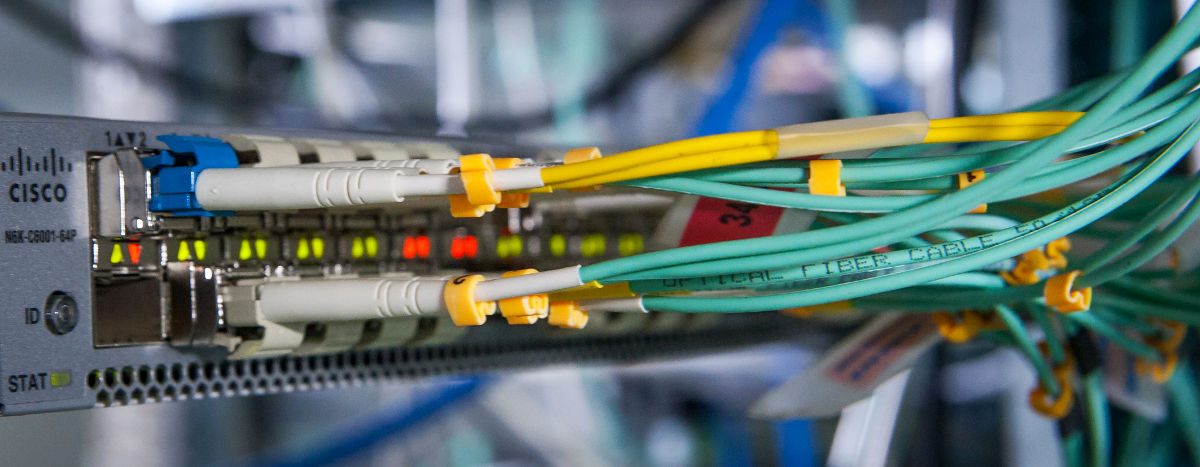
We usually see some products that are compliant with MSA when refers to fiber optic transceivers, but what does MSA mean? It seems like a standard that is used to define the optical transceiver. In fact, MSAs are not official standards organizations. Instead, they are agreements that equipment vendors assume when developing form factors for communications interfaces. These form factors, usually called the transceiver modules, are typically deployed in active electronics such as switches, servers and multiplexers. In this text, some knowledge of the MSA will be introduced.
We usually see some products that are compliant with MSA when refers to fiber optic transceivers, but what does MSA mean? It seems like a standard that is used to define the optical transceiver. In fact, MSAs are not official standards organizations. Instead, they are agreements that equipment vendors assume when developing form factors for communications interfaces. These form factors, usually called the transceiver modules, are typically deployed in active electronics such as switches, servers and multiplexers. In this text, some knowledge of the MSA will be introduced.
What is Multi-source Agreement?
MSA stands for multi-source agreement, which is an agreement between multiple manufacturers to make products which are compatible across vendors, acting as de facto standards, establishing a competitive market for interoperable products. Products that adhere to MSAs include optical transceivers (SFP, SFP+, XENPAK, QSFP, XFP, etc), fiber optic cables, and other networking devices. MSAs strictly define the operating characteristics of these optical transceivers so that system vendors may implement ports in their devices that allow MSA compliant transceivers produced by name brand, as well a third party vendors, to function properly. That is, transceivers may be purchased from any of the multiple sources in the open market, like Fiberstore. MSAs are also important in the cabling industry as the density, line speed, power consumption and typical costs of a MSA can strongly impact its success in the marketplace. This, in turn, can drive the choice for both connector and media type.
Why is Multi-source Agreement so Important?
Equipment vendors all rely on MSAs when designing their systems, ensuring interoperability and interchangeability between interface modules, that is every supplier can produce the transceiver modules with the same functions. For this reason, there are many module suppliers from which customers can choose freely. As we all know, freedom of choice is the foundation of the efficient operation of markets. In order to gain a bigger share of the market, suppliers may act as efficiently as possible, which may drive down costs and offer the widest options to customers. Besides, since there are so many excellent 3rd party optical transceiver module suppliers in the market that network operators don’t need to purchase optical transceivers directly from system (original brand) vendors, which will also save huge costs. Finally, there is no doubt that all these will help support and encourage creation and adherence to standards at the same time. Over the past decade, the MSA process has helped accelerate the acceptance of modules such as SFP+ and CFP, which allow optical transceivers to support greater bandwidth such as 40G and 100G.
Approved Fiber Optica Transceiver Multi-source Agreements
MSA is a popular industry format jointly developed and supported by many network component vendors, most common optical transceivers are specified by it at present. MSAs usually specify parameters for optical transceivers and their guideline values, such as the electrical and optical interfaces (e.g. SX, LX, EX, ZX, etc), mechanical dimensions, electro-magnetic values and other data. This data is accessible by the host system over the I2C interface, as is the status of the optional DDM functions. Some approved fiber optica transceiver multi-source agreements are listed in the table below:
| Name | Year | Brief Description | Keywords/Applications |
| GBIC | 2000 | GigaBit Interface Converter | Designed for Gigabit Ethernet, SDH/SONET (2.5 Gb/s) and Fibre Channel (4Gb/s). Superseded by SFP |
| SFP | 2001 | Small Form-factor Pluggable | Designed for Gigabit Ethernet, SDH/SONET (2.5 Gb/s) and Fibre Channel (4Gb/s) |
| XENPAK | 2001 | Fiber optic transceiver for 10Gb Ethernet | Superseded by X2 and SFP+ |
| X2 | 2005 | Fiber optic transceiver for 10Gb Ethernet | Superseded by SFP+ |
| XFP | 2005 | Fiber optic transceiver for 10Gb Ethernet | Designed for 10Gb/s. Supports 8Gb/s Fibre Channel, 10 Gb/s Ethernet and Optical Transport Network |
| SFP+ | 2013 | Fiber optic transceiver for 10Gb Ethernet | Designed for 10Gb/s. Supports 8Gb/s Fibre Channel, 10 Gb/s Ethernet and Optical Transport Network standard OTU2 |
| QSFP/QSFP+ | 2013 | Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable 40G | Supports Ethernet, Fibre Channel, InfiniBand and SONET/SDH standards up to 40GB/s and 100Gb/s |
| CFP | 2013 | C Form Factor Pluggable (100G) | Optical transceiver form factors supporting 40Gb/s and 100Gb/s. CFP, CFP2 and CFP4 |
| CXP | In Progress | C Form Factor Pluggable | Supports Infiniband and Ethernet to 100G. CXP and CXP2 |