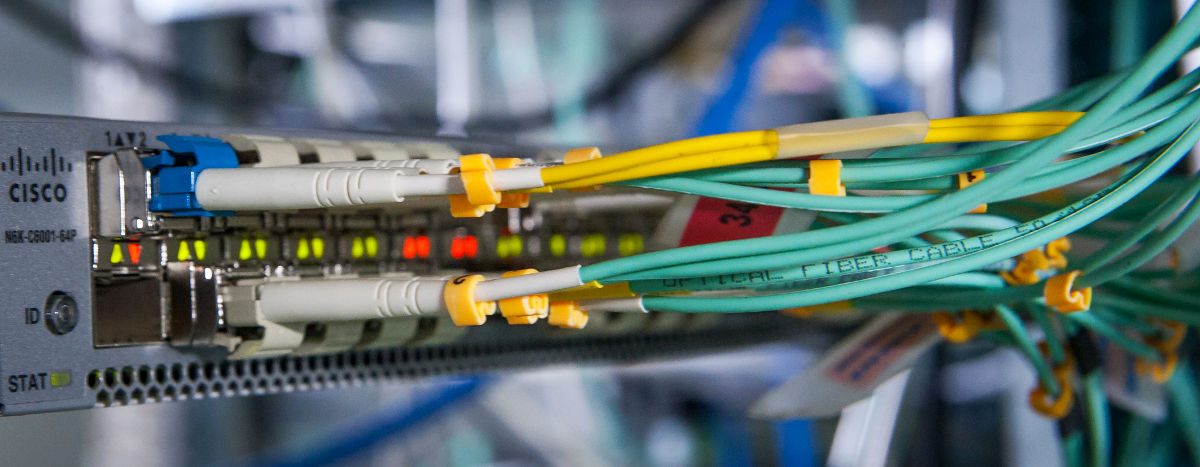
Multi-mode patch cord optical loss power measurement is performed using the steps described in ANSI/TIA-526-14,method A. The patch cord is substituted for the cable plant. Because patch cords are typically no longer than 5 m, the loss for the optical fiber is negligible and testing can be performed at 850 nm or 1300 nm. The loss measured in this test is the loss for the patch cord connector pair. ANSI/TIA-568-C.3 states that the maximum loss for a connector pair is 0.75 db.
After setting up the test equipment as described in ANSI/TIA-526-14, method A, clean and inspect the connectors at the ends of the fiber patch cord to be tested. Verify that your test jumpers have the same optical fiber type and connectors as the patch cords you are going to test. The ANSI/TIA-526-14 being used for testing. Ensure that there are no sharp bends in the test jumpers or patch cords during testing.
Because both patch cord connectors are easily accessible, optical power loss should be measured in both directions. The loss for the patch cord is the average of the two measurements. If the loss for the patch cord exceeds 0.75dB in either direction, the patch cord needs to be repaired or replaced.
Connector insertion loss measurement isolates the loss of a single connector on a cable assembly. It may be referred to as connector loss. Many time cable assemblies are shipped from the manufacturer with the insertion loss for each connector listed on the packaging. The package shown in Figure 33.37 contains a duplex multi-mode patch cord. In the upper-left corner of the package, a label lists the insertion loss measurements for each connector.
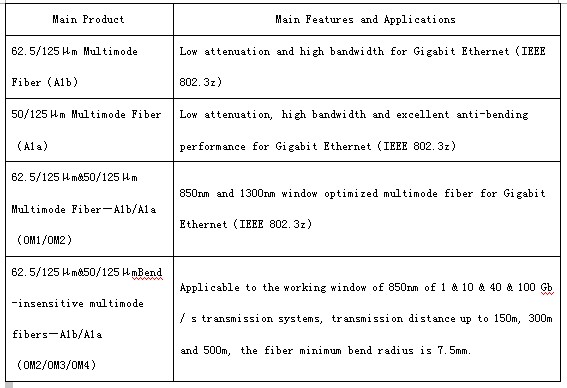
Connector test jumper 1 as shown earlier in Figure 33.31. Record the optical power displayed by the optical power meter. This number is the reference power measurement. This number is typically around -20dBm with a 62.5/125μm multimode optical fiber and -23.5dBm with a 50/125μm multimode optical fiber. These numbers can vary from OLTS to OLTS. The following are 62.5/125μm and 50/125μm multimode fiber from fiberstore, picture is below:
SC-SC Plenum Duplex 62.5/125 Multi-mode Fiber Patch Cable, with SC to SC termination, this fiber optic patch cable is specificially designed for ethernet, multimedia, or communication applications. The SC connector features a push-pull locking system. The plenum rating provides the fire protection required to run this cable within walls and air plenums without using conduit. The patented injection molding process provides each connection greater durability in resisting pulls, strains and impacts from cabling installs.
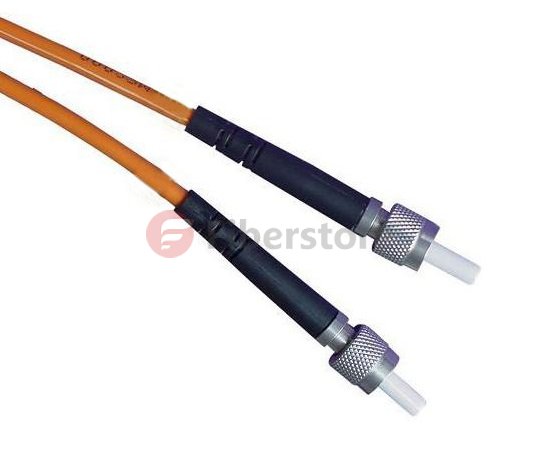
ST Fiber Cable connector has a bayonet-style housing and a long spring-loaded ferrule hold the fiber. They are available in both multi-mode or single mode versions. Horizontally mounted simplex and duplex adapters are available with metal or plastic housing.