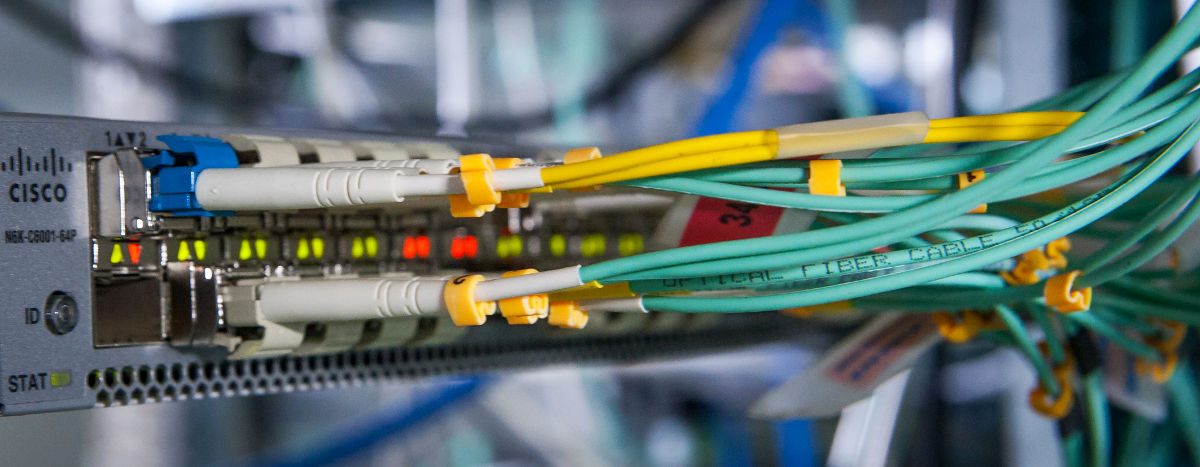
Corning and Lucent and other large companies proposed a “new generation of multi-mode fiber” concept to the international standardization bodies. A new generation of multimode fiber patch cable standards drafted by the International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO / IEC) and the Telecommunications Industry Alliance (TIA-TR42). As a new generation of multimode fiber transmission medium 10Gb / s Ethernet, be included in IEEE 10Git / s Ethernet standard. This article will briefly describe the new generation of multimode fiber patch cable critical technology.
1.1 The Typle of Multimode Fiber Patch Cable
The new generation of multimode fiber patch cable is 50/125μm, graded-index multimode fiber distribution. The number of this transmission mode Fiber Optic Cables is approximately 62.5μm multimode fiber transmission mode 1/2.5. This can effectively reduce the dispersion of the multimode fiber mode, increase the bandwidth. For 850nm wavelength, 50/125μm Multimode fiber bandwidth is 500MHz.km. Recent experiments confirmed: the use of 850nm vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) as a light source in the 1Gb / s rate, 50μm multimode fiber core diameter standard error can be no transfer 1750m, 50μm core diameter multimode fiber can be a new generation of error-free transmission 2000m. In the 10Gb / s down, 50μm core diameter multimode fiber can transmit a new generation of 600m. A new generation of multi-mode fiber is mainly used to support high-speed Ethernet (Ethernet), Fibre Channel (FC) and fiber optic interconnection (OIF). Meanwhile at 10Gbit / s system can transmit 600m, so that it can be used for building backbone and campus backbone extraordinary distance from the middle. In the data center design, within a distance of 100m to support higher speed (40G and 100Gbits / s? Ethernet, 16G and 32Gbits / s Fibre Channel) data transmission requirements.
The related products about New Generation multimode mode fiber patch cable, SMA905-ST Duplex 50/125 Dia2.5mm OM2 multimode fiber patch cable from fs.com, the products picture is below:

The SMA-905 fiber optic patch cord, also known as FSMA connector, was one of the First fiber optic interconnect system that gained industry wide acceptance.SMA905 fiber patch cords make use of threaded connections and is still widely used for military, industrial, medical and Surgical applications and laser systems because of their low cost multimode coupling. It features simple termination and Assembly, and is TIA and IEC compliant. SMA 905 multimode connectors are available with stainless alloy or stainless steel ferrules.
1.2 A New Generation of Multimode Fiber Source
Traditional multimode fiber networks use light-emitting diode (LED) as light source . In low-speed network, which is an economically rational choice. However, LED is spontaneous emission light, the radiation -emitting laser is excited , the carrier lifetime is longer the former than the latter, and thus the LED modulation rate is limited , and not more than gigabit networks. Further, LED compared with a laser, the beam divergence angle, wide spectral width . After injection of multimode fiber , excite more high-order mode, the introduction of more wavelength components, so that the fiber bandwidth decreases . Fortunately 850nm vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) not only has the advantage of these lasers, but aslo the price is basically the same with the LED. Other advantages of VCSEL are: low threshold current, may not be enlarged, driven directly by logic gates at 10Gb / s rate, get a few milliwatts of output power; emission wavelength of 850nm which does not apply to the standard single-mode fiber just for multimode fiber . At this wavelength, an inexpensive silicon detectors can be used and have a good frequency response; VCSEL another remarkable advantage is that the manufacturing process can be easily controlled distribution of the emitted light power , which is very advantageous for improving the bandwidth of MMF. It is because of these advantages, the new generation of multimode fiber standard will use 850nm VCSEL light source .
1.3 The Bandwidth Distance of Multimode Fiber Patch Cable
By comparing the above- described laser and LED , the use of multimode fiber laser light source, the transmission bandwidth should be greatly improved. However, experimental results show that simply make the bandwidth of a laser instead of LED light source, system is not only reduced but increased. IEEE Expert Group found through research, the bandwidth of multimode fiber and the optical fiber or the injection molding state of a power distribution. The preform fabrication process, the refractive index of the fiber axis prone to depression. Done before light source LED, is overfilled launch (OFL-Over Filled Launch), all of the fiber mode ( hundreds ) are excited to bring their own part of each module power. The refractive index of the fiber center delay characteristic distortion affects only a small number of models, the relatively limited impact on the modal bandwidth of the fiber. The measured multimode fiber bandwidth for the use of LED light source system is correct. However, when a laser light source, a laser beam spot is only a few microns, the divergence angle is smaller than the LED, so that only a small number of modes excited in the center of the fiber transmission, each mode carries a large part of the power, the refractive index of the fiber center distortion affect a small number of patterns of delay characteristics, so that decreased multimode fiber bandwidth. So it can not be measured with a laser light source for multimode fiber OFL bandwidth of conventional methods.
Today a new generation of multi-mode fiber main measurement bandwidth limit die by injection method (RML-Restricted Mode Launch). In this way the measured bandwidth is called ” laser -bandwidth ” or ” modal bandwidth limit “, previously done with the LED light source measured bandwidth is called “OFL bandwidth is .” Both represent the bandwidth of multimode fiber laser and LED light source with a time of injection. August 5, 2009, TIA Standards Committee released a new generation of bandwidth distance product standard multimode fiber , 850nm laser distance -bandwidth product of 470MHz.km, 850nm OFL bandwidth of distance product of 350MHz.km, 1300nm OFL bandwidth of distance plot to 500MHz.km. Incidentally, the bandwidth from the product of the above-described generation of the multi-mode fiber is only 3dB corresponding baseband bandwidth of multimode fiber, multimode fiber does not take more than a high-frequency band -pass region is also used when the transmission signal . Today, by orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) technology , can make good use of multimode optical fiber through a high frequency band region , under conditions of use of the same fiber optic patch cable type, transmission using high frequency band signal through region greatly improved multi-mode fiber transmission capacity.
1.4 Source Injection Method
In actual use, the multimode fiber coupled laser and the following methods:
Bias injection: In order to avoid the deterioration of these lasers is injected directly into the bandwidth MMF appears, use the mode regulator
Connection (MCP Mode Conditioning Patch Cable), the laser output is coupled into a multimode fiber. Connection-mode regulator is a short Single Mode Fiber Cable, one end of which is coupled with the laser and the other end coupled to a multimode optical fiber. SMF output spot detouring from the multimode fiber axis at a distance, allowing the deviation from the range is 17 ~ 24μm, the aim is to avoid the center of the refractive index depression, but do not deviate too far, only one group is selectively lower-order mode excitation .
Centre injection: ideal for the refractive index profile, there is no central depression MMF can be used instead of the center of the injection molding
Regulator connection. The advantage of this is that the bandwidth of the laser can effectively improve the MMF to reduce the complexity of the network system and reduce system cost, a current-mode regulator 80 to the connection of approximately U.S. $ 100. Corning launched InfiniCor CL 1000 (62.5μm core diameter) and InfiniCor CL 2000 (50μm core diameter) is Gigabit Ethernet 1300nm wavelength laser directly into the mode without adjusting the first multi-connection mode fiber.