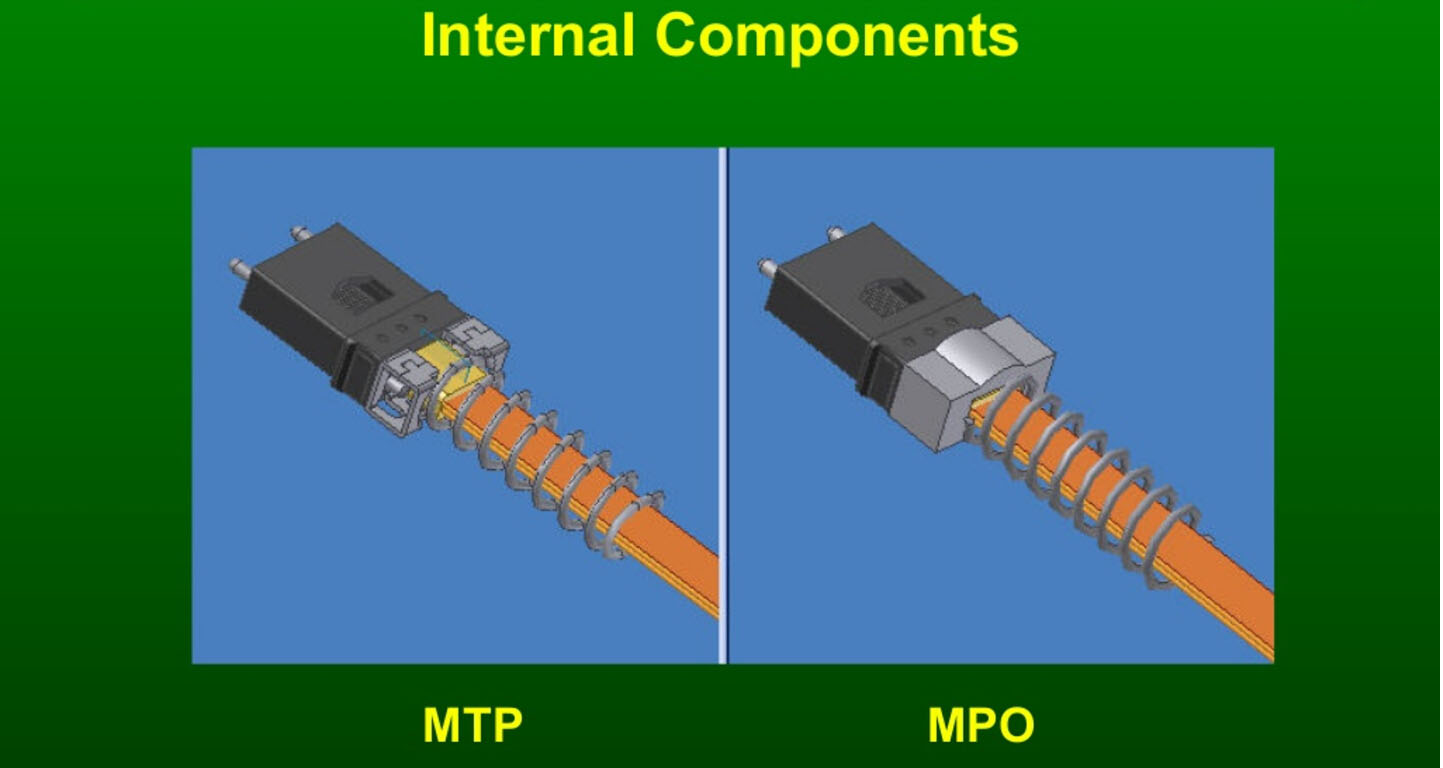
In regard to multi-fiber connector, many will think of MTP connector while the others will think it is MPO connector. In most cases, these two kinds of connectors can be considered the same. Actually, they are a little different not only in names but also in some other aspects. MTP VS MPO: what’s the difference? This post will clarify the differences between these two.
As the industry acronym for “Multi-fiber Push On”, MPO is developed to provide multi-fiber connection in one connector to support higher bandwidth and higher density applications. MPO connector is standardized in the international regulatory framework (the IEC 61754-7 standard) and the U.S. (TIA-604-5 Standard ). At present, the most common fiber counts are 12 and 24, and 48 to 72 fiber counts are also possible in limited applications.
MTP is a registered trade mark of US Conec. In other words, MTP connector is used by US Conec to describe their multi-fiber connector initially. Now MTP is commonly referred to as a high performance MPO connector. So MTP connectors are fully compliance with all generic MPO connectors and can interconnect directly with other MPO based infrastructures.
As mentioned above, MTP connector is an enhanced version of MPO connector. This means Generic MPO connectors are limited in performance and are not able to offer the high performance levels of MTP connectors. Generally, MTP connectors are superior to generic MPO connectors in the following aspects:
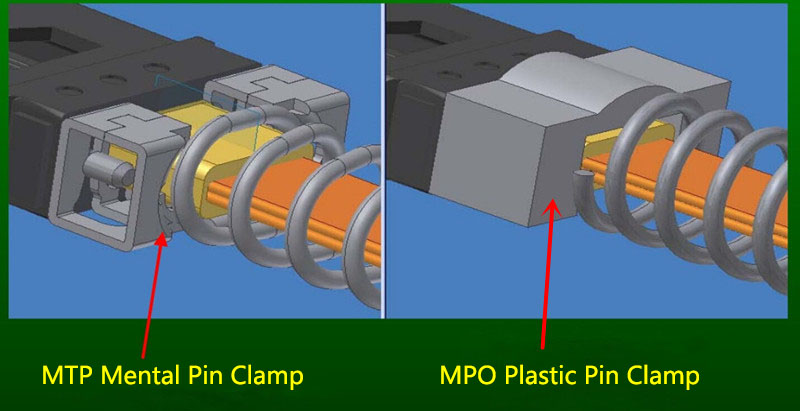
The MTP connector has a metal pin clamp to ensure a strong clasp on the pins and minimize any inadvertent breaking when mating connectors. While MPO connectors are often manufactured with inferior plastic pin clamps which may lead to effortless breaking of pins with constant cable mating.
An important feature of MTP is its floating ferrule, which will help to improve mechanical performance. To be specific, The MT ferrule of MTP connectors can float inside to keep physical contact over a mated pair under an applied load. Generic MPO connector do not have this ferrule float feature.
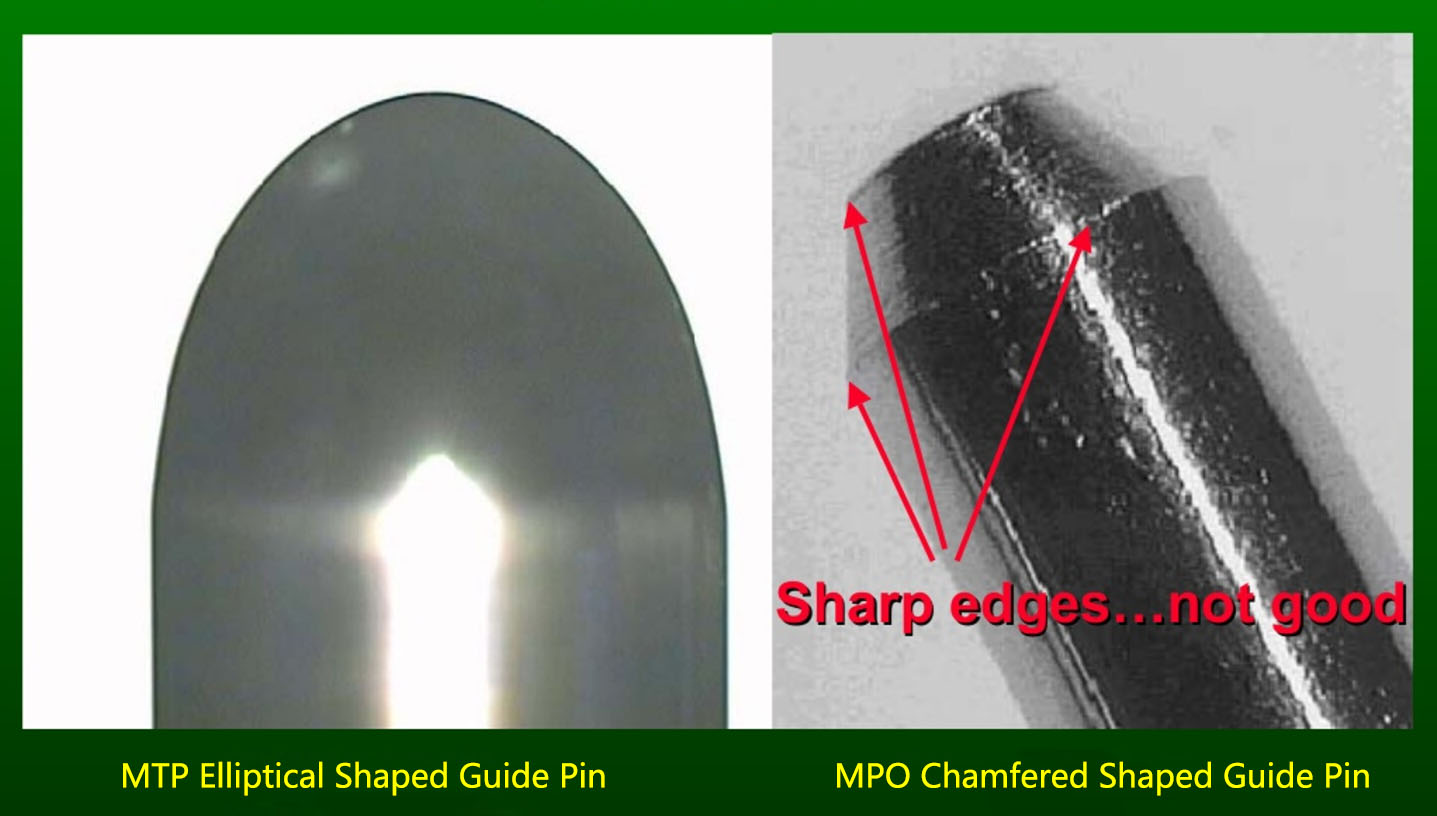
MTP connectors use tightly held tolerance stainless steel elliptical guide pin tips to reduce guide hole wear. Unlike single fiber connectors, the adapters for multi-fiber connectors are only for coarse alignment. Thus the guide pins are critical for accurate alignment when mating two MT ferrules. The elliptical shaped pins of MTP connectors does not chip the ferrule material which helps to reduce the amount of debris that may fall into the guide pin holes or on the ferrule end face. Generic MPO connectors have chamfered shaped guide pins which will produce more debris when used.
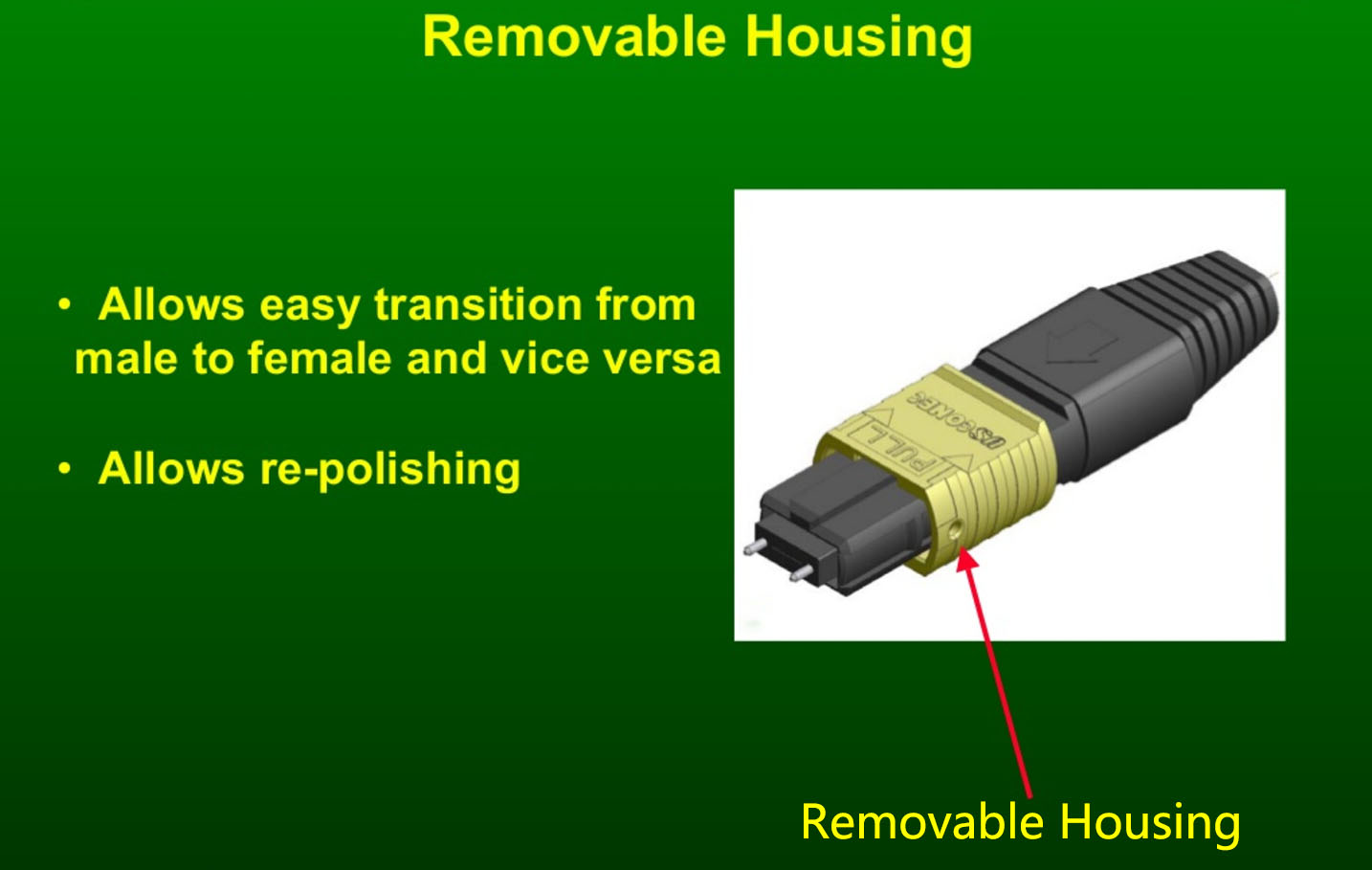
The MTP connector is designed to have a removable housing. This allows users to re-work and re-polish the MT ferrule, to easily get access to performance testing and to smoothly change the gender after assembly or even in the field.
The generic MPO connector is recognized as an international standard for network architects who require density and strive for shorter install times, as well as simplified cabling infrastructure for their 40G/100G data centers. However, in higher fiber count MPO cabling, using MPO connectors will have problems with optical loss (measured in dB), dropped packets and diminished network visibility.
The MTP connector is a high performance MPO connector with multiple engineered product enhancements to improve optical and mechanical performance. It is designed to ensure the precision alignment of the female and male sides. This is critical to reducing insertion loss and return loss in dense, multi-mode fiber connectivity. MTP/MPO connector
MTP VS MPO: Do you know the differences between them now? They are both widely used in high density cabling networks, especially in 40G/100G data centers. MPO is an internationally recognized standard interface for connector manufacturers. While MTP is one type of MPO connector. It is a brand owned by US Conec. If you are planning to build a multi-fiber network, a cable with MTP connectors will give you the best over-life performance. MPO connectors will also work, but may not perform to the same level.
Related Article: MTP/MPO Connector: Difference And Cleaning Recommendation
MTP/MPO Cable Assembly – the Game Changer of Data Center Cabling